Page 178 - Entrophy Analysis in Thermal Engineering Systems
P. 178
Exergy 173
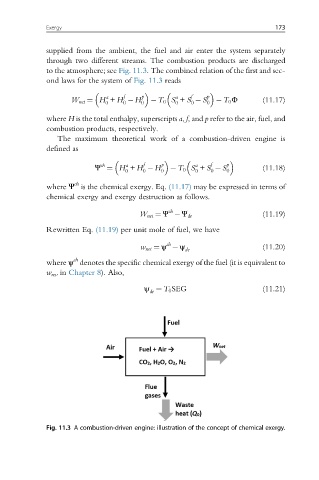
supplied from the ambient, the fuel and air enter the system separately
through two different streams. The combustion products are discharged
to the atmosphere; see Fig. 11.3. The combined relation of the first and sec-
ond laws for the system of Fig. 11.3 reads
f p f p T 0 Φ
a a (11.17)
0
0
0
0
W net ¼ H + H H 0 T 0 S + S S 0
where H is the total enthalpy, superscripts a, f, and p refer to the air, fuel, and
combustion products, respectively.
The maximum theoretical work of a combustion-driven engine is
defined as
f p f p
ch a a (11.18)
0
0
0
0
Ψ ¼ H + H H 0 T 0 S + S S 0
where Ψ is the chemical exergy. Eq. (11.17) may be expressed in terms of
ch
chemical exergy and exergy destruction as follows.
(11.19)
ch
W net ¼ Ψ Ψ de
Rewritten Eq. (11.19) per unit mole of fuel, we have
w net ¼ ψ ψ (11.20)
ch
de
where ψ denotes the specific chemical exergy of the fuel (it is equivalent to
ch
w rev in Chapter 8). Also,
ψ ¼ T 0 SEG (11.21)
de
Fig. 11.3 A combustion-driven engine: illustration of the concept of chemical exergy.