Page 61 - Environmental Nanotechnology Applications and Impacts of Nanomaterials
P. 61
Nanomaterials Fabrication 47
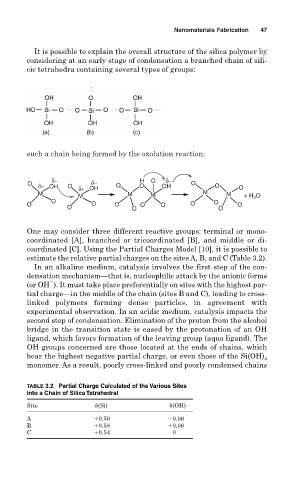
It is possible to explain the overall structure of the silica polymer by
considering at an early stage of condensation a branched chain of sili-
cic tetrahedra containing several types of groups:
such a chain being formed by the oxolation reaction:
δ− H O δ−
δ−
O δ+ OH O δ+ OH O O OH O O O
M M M M M
M + H 2 O
O O
O O O O O O O
O O O
One may consider three different reactive groups: terminal or mono-
coordinated [A], branched or tricoordinated [B], and middle or di-
coordinated [C]. Using the Partial Charges Model [10], it is possible to
estimate the relative partial charges on the sites A, B, and C (Table 3.2).
In an alkaline medium, catalysis involves the first step of the con-
densation mechanism—that is, nucleophilic attack by the anionic forms
(or OH ). It must take place preferentially on sites with the highest par-
tial charge—in the middle of the chain (sites B and C), leading to cross-
linked polymers forming dense particles, in agreement with
experimental observation. In an acidic medium, catalysis impacts the
second step of condensation. Elimination of the proton from the alcohol
bridge in the transition state is eased by the protonation of an OH
ligand, which favors formation of the leaving group (aquo ligand). The
OH groups concerned are those located at the ends of chains, which
bear the highest negative partial charge, or even those of the Si(OH) 4
monomer. As a result, poorly cross-linked and poorly condensed chains
TABLE 3.2 Partial Charge Calculated of the Various Sites
into a Chain of Silica Tetrahedral
Site (Si) (OH)
A 0.50 0.06
B 0.58 0.06
C 0.54 0