Page 144 - Flexible Robotics in Medicine
P. 144
130 Chapter 5
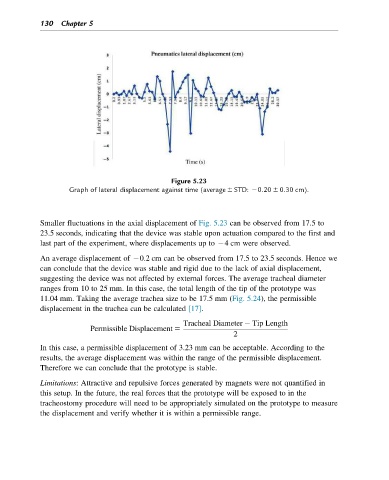
Figure 5.23
Graph of lateral displacement against time (average 6 STD: 20.20 6 0.30 cm).
Smaller fluctuations in the axial displacement of Fig. 5.23 can be observed from 17.5 to
23.5 seconds, indicating that the device was stable upon actuation compared to the first and
last part of the experiment, where displacements up to 24 cm were observed.
An average displacement of 20.2 cm can be observed from 17.5 to 23.5 seconds. Hence we
can conclude that the device was stable and rigid due to the lack of axial displacement,
suggesting the device was not affected by external forces. The average tracheal diameter
ranges from 10 to 25 mm. In this case, the total length of the tip of the prototype was
11.04 mm. Taking the average trachea size to be 17.5 mm (Fig. 5.24), the permissible
displacement in the trachea can be calculated [17].
Tracheal Diameter Tip Length
Permissible Displacement 5
2
In this case, a permissible displacement of 3.23 mm can be acceptable. According to the
results, the average displacement was within the range of the permissible displacement.
Therefore we can conclude that the prototype is stable.
Limitations: Attractive and repulsive forces generated by magnets were not quantified in
this setup. In the future, the real forces that the prototype will be exposed to in the
tracheostomy procedure will need to be appropriately simulated on the prototype to measure
the displacement and verify whether it is within a permissible range.