Page 121 - Fluid Mechanics and Thermodynamics of Turbomachinery
P. 121
102 Fluid Mechanics, Thermodynamics of Turbomachinery
Thus,
c x
R D .tan ˇ 3 tan ˇ 2 / (4.22a)
2U
or
1 c x
R D C .tan ˇ 3 tan ˛ 2 /, (4.22b)
2 2U
after using eqn. (4.21).
If ˇ 3 D ˇ 2 , the reaction is zero; if ˇ 3 D ˛ 2 the reaction is 50%. These two special
cases are discussed below in more detail.
Zero reaction stage
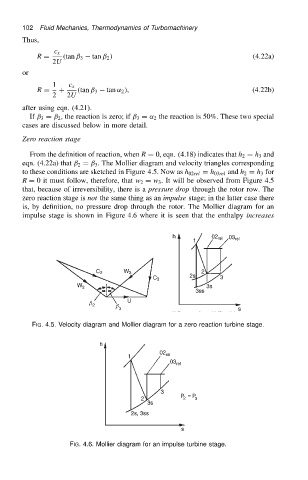
From the definition of reaction, when R D 0, eqn. (4.18) indicates that h 2 D h 3 and
eqn. (4.22a) that ˇ 2 D ˇ 3 . The Mollier diagram and velocity triangles corresponding
to these conditions are sketched in Figure 4.5. Now as h 02rel D h 03rel and h 2 D h 3 for
R D 0 it must follow, therefore, that w 2 D w 3 . It will be observed from Figure 4.5
that, because of irreversibility, there is a pressure drop through the rotor row. The
zero reaction stage is not the same thing as an impulse stage; in the latter case there
is, by definition, no pressure drop through the rotor. The Mollier diagram for an
impulse stage is shown in Figure 4.6 where it is seen that the enthalpy increases
FIG. 4.5. Velocity diagram and Mollier diagram for a zero reaction turbine stage.
FIG. 4.6. Mollier diagram for an impulse turbine stage.