Page 134 - Fluid Mechanics and Thermodynamics of Turbomachinery
P. 134
Axial-flow Turbines: Two-dimensional Theory 115
operating range of the turbine. This means obtaining a blade design in which none
of its natural frequencies coincides with any excitation frequency. The subject is
complex, interesting but outside of the scope of the present text.
Centrifugal stresses
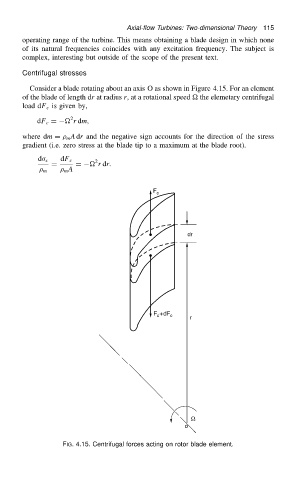
Consider a blade rotating about an axis O as shown in Figure 4.15. For an element
of the blade of length dr at radius r, at a rotational speed the elemetary centrifugal
load dF c is given by,
2
dF c D r dm,
where dm D m A dr and the negative sign accounts for the direction of the stress
gradient (i.e. zero stress at the blade tip to a maximum at the blade root).
d c dF c 2
D D r dr.
m m A
F c
dr
F +dF c
c
r
W
o
FIG. 4.15. Centrifugal forces acting on rotor blade element.