Page 277 - Fluid Mechanics and Thermodynamics of Turbomachinery
P. 277
258 Fluid Mechanics, Thermodynamics of Turbomachinery
1.1
1.0
h/h opt
ZL/D 2
0.9
6.0
3.0 4.0 4.5 5.0
0.8
1.5 2.0 2.5 3.0
r /r
2 3rms
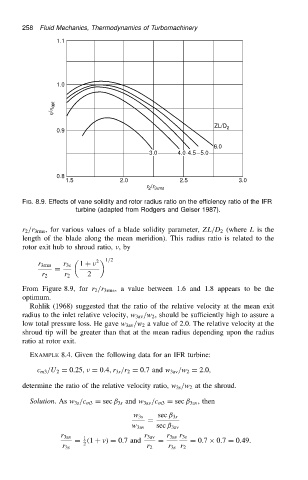
FIG. 8.9. Effects of vane solidity and rotor radius ratio on the efficiency ratio of the IFR
turbine (adapted from Rodgers and Geiser 1987).
r 2 /r 3rms , for various values of a blade solidity parameter, ZL/D 2 (where L is the
length of the blade along the mean meridion). This radius ratio is related to the
rotor exit hub to shroud ratio, ,by
2 1/2
r 3rms r 3s 1 C
D
r 2 r 2 2
From Figure 8.9, for r 2 /r 3rms , a value between 1.6 and 1.8 appears to be the
optimum.
Rohlik (1968) suggested that the ratio of the relative velocity at the mean exit
radius to the inlet relative velocity, w 3av /w 2 , should be sufficiently high to assure a
low total pressure loss. He gave w 3av /w 2 a value of 2.0. The relative velocity at the
shroud tip will be greater than that at the mean radius depending upon the radius
ratio at rotor exit.
EXAMPLE 8.4. Given the following data for an IFR turbine:
c m3 /U 2 D 0.25, D 0.4,r 3s /r 2 D 0.7 and w 3av /w 2 D 2.0,
determine the ratio of the relative velocity ratio, w 3s /w 2 at the shroud.
Solution.As w 3s /c m3 D sec ˇ 3s and w 3av /c m3 D sec ˇ 3av , then
w 3s sec ˇ 3s
D
w 3av sec ˇ 3av
r 3av 1 r 3av r 3av r 3s
D .1 C v/ D 0.7 and D D 0.7 ð 0.7 D 0.49.
2
r 3s r 2 r 3s r 2