Page 281 - Fluid Mechanics and Thermodynamics of Turbomachinery
P. 281
262 Fluid Mechanics, Thermodynamics of Turbomachinery
0.6
(l - cos n i)
0.4
n = 1.75
n = 2.5
(i < 0)
(i > 0)
0.2
-60 -40 -20 0 20 40 60
Incidence angle, i (deg)
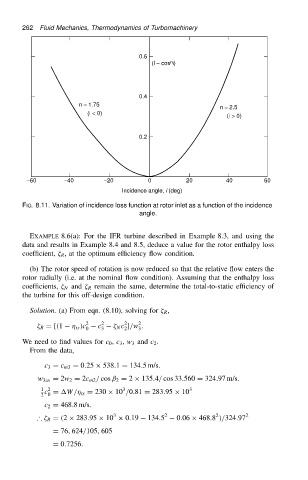
FIG. 8.11. Variation of incidence loss function at rotor inlet as a function of the incidence
angle.
EXAMPLE 8.6(a): For the IFR turbine described in Example 8.3, and using the
data and results in Example 8.4 and 8.5, deduce a value for the rotor enthalpy loss
coefficient, R , at the optimum efficiency flow condition.
(b) The rotor speed of rotation is now reduced so that the relative flow enters the
rotor radially (i.e. at the nominal flow condition). Assuming that the enthalpy loss
coefficients, N and R remain the same, determine the total-to-static efficiency of
the turbine for this off-design condition.
Solution. (a) From eqn. (8.10), solving for R ,
2
2
R D [.1 ts /c 2 c 2 N c ]/w .
0 3 2 3
We need to find values for c 0 , c 3 , w 3 and c 2 .
From the data,
c 3 D c m3 D 0.25 ð 538.1 D 134.5 m/s.
w 3av D 2w 2 D 2c m2 / cos ˇ 2 D 2 ð 135.4/ cos 33.560 D 324.97 m/s.
1 2 3 3
c D W/ ts D 230 ð 10 /0.81 D 283.95 ð 10
2 0
c 2 D 468.8 m/s.
2
3
∴ R D .2 ð 283.95 ð 10 ð 0.19 134.5 2 0.06 ð 468.8 //324.97 2
D 76, 624/105, 605
D 0.7256.