Page 215 - Subyek Teknik Mesin - Forsthoffers Best Practice Handbook for Rotating Machinery by William E Forsthoffer
P. 215
Compressor Best Practices Best Practice 3 .22
A. The supply system that directly feed into a bearing, the atmospheric bushing
downstream pressure will be constant, at approximately 138
This system consists of the reservoir, pumping units, ex- kPa (20 psi). However, the upstream supply pressure will vary
changers, transfer valves, temperature control valves, and filters. with the pressure required by the sealing media in the
The purpose of this sub-system is to continuously supply clean, compressor.
cool sealing fluid to the seal interfaces at the correct differential As an example, if a seal system is designed to maintain
pressure. a constant differential of 34.5 kPa (5 psi) per square inch be-
tween the compressor process gas and the seal oil supply to the
gas side bushing, the supply pressure with zero process gas
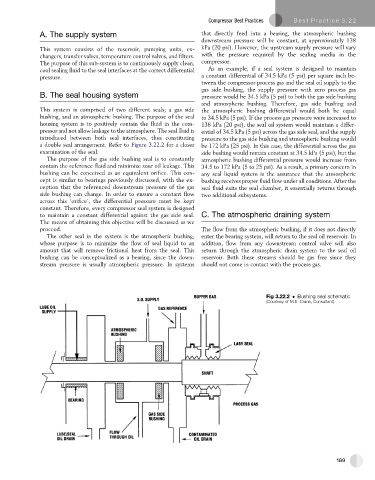
B. The seal housing system pressure would be 34.5 kPa (5 psi) to both the gas side bushing
and atmospheric bushing. Therefore, gas side bushing and
This system is comprised of two different seals; a gas side the atmospheric bushing differential would both be equal
bushing, and an atmospheric bushing. The purpose of the seal to 34.5 kPa (5 psi). If the process gas pressure were increased to
housing system is to positively contain the fluid in the com- 138 kPa (20 psi), the seal oil system would maintain a differ-
pressor and not allow leakage to the atmosphere. The seal fluid is ential of 34.5 kPa (5 psi) across the gas side seal, and the supply
introduced between both seal interfaces, thus constituting pressure to the gas side bushing and atmospheric bushing would
a double seal arrangement. Refer to Figure 3.22.2 for a closer be 172 kPa (25 psi). In this case, the differential across the gas
examination of the seal. side bushing would remain constant at 34.5 kPa (5 psi), but the
The purpose of the gas side bushing seal is to constantly atmospheric bushing differential pressure would increase from
contain the reference fluid and minimize sour oil leakage. This 34.5 to 172 kPa (5 to 25 psi). As a result, a primary concern in
bushing can be conceived as an equivalent orifice. This con- any seal liquid system is the assurance that the atmospheric
cept is similar to bearings previously discussed, with the ex- bushing receives proper fluid flow under all conditions. After the
ception that the referenced downstream pressure of the gas seal fluid exits the seal chamber, it essentially returns through
side bushing can change. In order to ensure a constant flow two additional subsystems.
across this ‘orifice’, the differential pressure must be kept
constant. Therefore, every compressor seal system is designed
to maintain a constant differential against the gas side seal. C. The atmospheric draining system
The means of obtaining this objective will be discussed as we
proceed. The flow from the atmospheric bushing, if it does not directly
The other seal in the system is the atmospheric bushing, enter the bearing system, will return to the seal oil reservoir. In
whose purpose is to minimize the flow of seal liquid to an addition, flow from any downstream control valve will also
amount that will remove frictional heat from the seal. This return through the atmospheric drain system to the seal oil
bushing can be conceptualized as a bearing, since the down- reservoir. Both these streams should be gas free since they
stream pressure is usually atmospheric pressure. In systems should not come in contact with the process gas.
Fig 3.22.2 Bushing seal schematic
(Courtesy of M.E. Crane, Consultant)
189