Page 222 - Subyek Teknik Mesin - Forsthoffers Best Practice Handbook for Rotating Machinery by William E Forsthoffer
P. 222
Be st Practice 3 .22 Compressor Best Practices
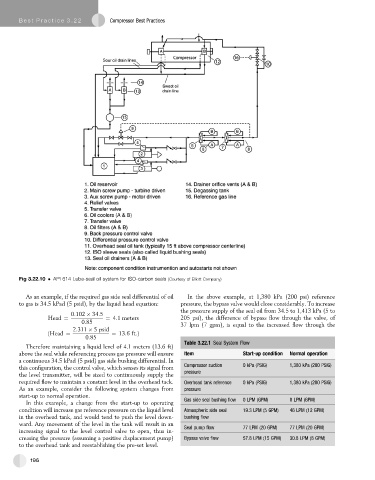
Fig 3.22.10 API 614 Lube-seal oil system for ISO-carbon seals (Courtesy of Elliott Company)
As an example, if the required gas side seal differential of oil In the above example, at 1,380 kPa (200 psi) reference
to gas is 34.5 kPad (5 psid), by the liquid head equation: pressure, the bypass valve would close considerably. To increase
the pressure supply of the seal oil from 34.5 to 1,413 kPa (5 to
0:102 34:5
Head ¼ ¼ 4:1 meters 205 psi), the difference of bypass flow through the valve, of
0:85 37 lpm (7 gpm), is equal to the increased flow through the
2:311 5 psid
ðHead ¼ ¼ 13:6ft:Þ
0:85
Table 3.22.1 Seal System Flow
Therefore maintaining a liquid level of 4.1 meters (13.6 ft)
above the seal while referencing process gas pressure will ensure Item Start-up condition Normal operation
a continuous 34.5 kPad (5 psid) gas side bushing differential. In
this configuration, the control valve, which senses its signal from Compressor suction 0 kPa (PSIG) 1,380 kPa (200 PSIG)
pressure
the level transmitter, will be sized to continuously supply the
required flow to maintain a constant level in the overhead tack. Overhead tank reference 0 kPa (PSIG) 1,380 kPa (200 PSIG)
As an example, consider the following system changes from pressure
start-up to normal operation. Gas side seal bushing flow 0 LPM (GPM) 0 LPM (GPM)
In this example, a change from the start-up to operating
condition will increase gas reference pressure on the liquid level Atmospheric side seal 19.3 LPM (5 GPM) 46 LPM (12 GPM)
in the overhead tank, and would tend to push the level down- bushing flow
ward. Any movement of the level in the tank will result in an Seal pump flow 77 LPM (20 GPM) 77 LPM (20 GPM)
increasing signal to the level control valve to open, thus in-
creasing the pressure (assuming a positive displacement pump) Bypass valve flow 57.8 LPM (15 GPM) 30.8 LPM (8 GPM)
to the overhead tank and reestablishing the pre-set level.
196