Page 300 - Subyek Teknik Mesin - Forsthoffers Best Practice Handbook for Rotating Machinery by William E Forsthoffer
P. 300
Steam Turbine Best Practices Be st Practice 5.6
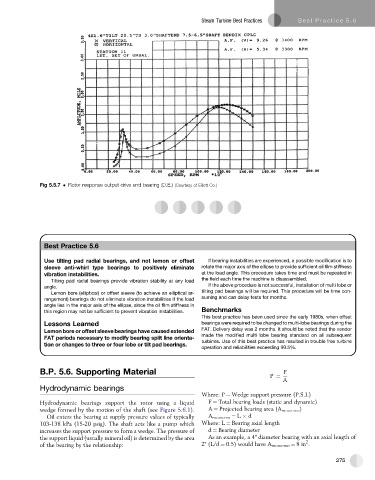
Fig 5.5.7 Rotor response output drive end bearing (D.E.) (Courtesy of Elliott Co.)
Best Practice 5.6Practice 5.6Practice 5.6
Best
Best
Use tilting pad radial bearings, and not lemon or offset If bearing instabilities are experienced, a possible modification is to
sleeve anti-whirl type bearings to positively eliminate rotate the major axis of the ellipse to provide sufficient oil film stiffness
vibration instabilities. at the load angle. This procedure takes time and must be repeated in
the field each time the machine is disassembled.
Tilting pad radial bearings provide vibration stability at any load
angle. If the above procedure is not successful, installation of multi lobe or
Lemon bore (elliptical) or offset sleeve (to achieve an elliptical ar- tilting pad bearings will be required. This procedure will be time con-
rangement) bearings do not eliminate vibration instabilities if the load suming and can delay tests for months.
angle lies in the major axis of the ellipse, since the oil film stiffness in
this region may not be sufficient to prevent vibration instabilities. Benchmarks
This best practice has been used since the early 1980s, when offset
Lessons Learned bearings were required to be changed to multi-lobe bearings during the
Lemon bore or offset sleeve bearings have caused extended FAT. Delivery delay was 2 months. It should be noted that the vendor
FAT periods necessary to modify bearing split line orienta- made the modified multi lobe bearing standard on all subsequent
turbines. Use of this best practice has resulted in trouble free turbine
tion or changes to three or four lobe or tilt pad bearings.
operation and reliabilities exceeding 99.5%.
B.P. 5.6. Supporting Material F
P ¼
A
Hydrodynamic bearings
Where: P ¼ Wedge support pressure (P.S.I.)
Hydrodynamic bearings support the rotor using a liquid F ¼ Total bearing loads (static and dynamic)
wedge formed by the motion of the shaft (see Figure 5.6.1). A ¼ Projected bearing area (A PROJECTED )
Oil enters the bearing at supply pressure values of typically A PROJECTED ¼ L d
103-138 kPa (15-20 psig). The shaft acts like a pump which Where: L ¼ Bearing axial length
increases the support pressure to form a wedge. The pressure of d ¼ Bearing diameter
the support liquid (usually mineral oil) is determined by the area As an example, a 4" diameter bearing with an axial length of
2
of the bearing by the relationship: 2" (L/d ¼ 0.5) would have A PROJECTED ¼ 8in .
275