Page 60 - Subyek Teknik Mesin - Forsthoffers Best Practice Handbook for Rotating Machinery by William E Forsthoffer
P. 60
Be st Practice 2 .3 Pump Best Practices
Head required e The required head that the pump must has published curves which can be used to calculate the per-
develop is based on the static pressure difference between the formance effects resulting from pumping viscous liquid.
discharge terminal point and the suction source, the elevation Vapor pressure and specific gravity influence the type of
difference and the friction losses through system components pump to use and its mechanical design configuration. Vapor
including suction and discharge side piping, pressure drop pressure is an important property when determining whether
through heat exchangers, furnaces, control valves and other there is adequate net energy available at the pump suction to
equipment. It is represented by the equation in Figure 2.3.1. avoid vaporization of the liquid which can lead to performance
deterioration and possible shortened life expectancy of the
pump.
Specific gravity is the liquid property used to calculate the
H = 10.2 ΔP (at pump flanges)
amount of head a pump has to produce to overcome the re-
S.G.
ΔP = Total pressure difference between the discharge system and sistance of the suction and discharge systems. It is also used as
suction system, measured at the pump flanges in barg a guideline to determine whether a pump casing design should
S.G. = Specific gravity of the liquid at pump temperature be of the vertical (radial) split or horizontal (axial) configuration
H = Pump required head in meter-Kg force/Kg mass (refer to Figure 2.3.2 for some guidelines).
Notes: If pressure is measured in KPa, constant = 0.102
2
If pressure is measured in Kg/cm , constant = 10.003
If pressure is measured in Psig, constant = 2.311 and head required
is measured in FT-LB force/LB mass Use radial split casing for:
S.G. 0.7 @ pumping temperature
Pumping temperature 200 C (400 F)
Fig 2.3.1 Required head equation Flammable or toxic liquids at rated discharge pressures above 6,896
Kpa (1000 psig)
Liquid properties e Viscosity, vapor pressure and specific
gravity each play an important role in achieving the required
Fig 2.3.2 Casing configuration guidelines
level of pump reliability within the operating system. Viscosity
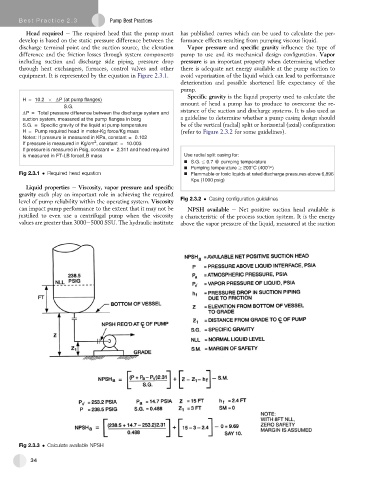
can impact pump performance to the extent that it may not be NPSH available e Net positive suction head available is
justified to even use a centrifugal pump when the viscosity a characteristic of the process suction system. It is the energy
values are greater than 3000e5000 SSU. The hydraulic institute above the vapor pressure of the liquid, measured at the suction
Fig 2.3.3 Calculate available NPSH
34