Page 62 - Subyek Teknik Mesin - Forsthoffers Best Practice Handbook for Rotating Machinery by William E Forsthoffer
P. 62
Be st Practice 2 .4 Pump Best Practices
Best Practice 2.4Practice 2.4Practice 2.4Practice 2.4
Best
Best
Best
State the required centrifugal pump casing design e hori- Lessons Learned
zontal split or radial and single or double volute e on the Leaving pump case design to the EP&C can lead to field
pump data sheet. safety and reliability issues.
Review pump vendor experience lists to determine field operating Not being proactive during preparation of the pump data sheets has
maximum pressures for horizontal split pumps and confirm acceptable allowed EP&Cs (contractors) and pump vendors to propose pumps
field operation with users above 10,342 kpa (1500 psi) operating that are a lower cost but expose the end user to field safety and re-
pressures. Select a radial split pump case if there are reports of hori- liability issues.
zontal split pump joint wear and leakage.
Single volute pumps will produce large radial forces on the rotor at Benchmarks
flow rates other than at the centrifugal pump best efficiency point
These guidelines have been followed since the mid-1970s in all pro-
which will increase pump vibration and reduce wear ring and throat
jects to ensure optimum pump field reliability. This best practice has
bushing life.
continually produced pumps with trouble free start-up and MTBFs in
Double volute pumps will minimize the rotor radial forces and
excess of 80 months.
should be used whenever available.
Confirm pump vendor availability of double volute design for all
centrifugal pumps prior to vendor selection.
B.P. 2.4. Supporting Material Every plant has a multitude of these types of pumps in opera-
tion. A brief description of the various designs found in oper-
ating plants follows. Refer to Table 2.4.1 for the application
Dynamic pumps limits of dynamic pumps.
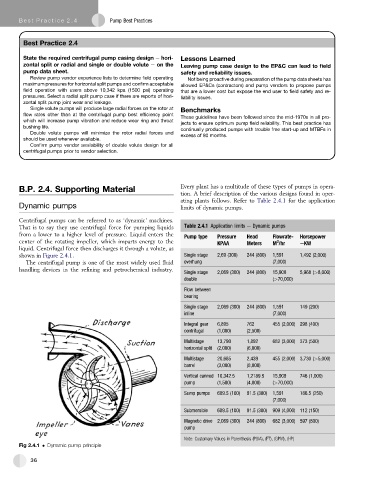
Centrifugal pumps can be referred to as ‘dynamic’ machines.
That is to say they use centrifugal force for pumping liquids Table 2.4.1 Application limits e Dynamic pumps
from a lower to a higher level of pressure. Liquid enters the Pump type Pressure Head Flowrate- Horsepower
3
center of the rotating impeller, which imparts energy to the KPAA Meters M /hr eKW
liquid. Centrifugal force then discharges it through a volute, as
shown in Figure 2.4.1. Single stage 2,69 (300) 244 (800) 1,591 1,492 (2,000)
The centrifugal pump is one of the most widely used fluid overhung (7,000)
handling devices in the refining and petrochemical industry.
Single stage 2,069 (300) 244 (800) 15,909 5,968 (>8,000)
double (>70,000)
Flow between
bearing
Single stage 2,069 (300) 244 (800) 1,591 149 (200)
inline (7,000)
Integral gear 6,895 762 455 (2,000) 298 (400)
centrifugal (1,000) (2,500)
Multistage 13,790 1,892 682 (3,000) 373 (500)
horizontal split (2,000) (6,000)
Multistage 20,685 2,439 455 (2,000) 3,730 (>5,000)
barrel (3,000) (8,000)
Vertical canned 10,342.5 1,2189.5 15,909 746 (1,000)
pump (1,500) (4,000) (>70,000)
Sump pumps 689.5 (100) 91.5 (300) 1,591 186.5 (250)
(7,000)
Submersible 689.5 (100) 91.5 (300) 909 (4,000) 112 (150)
Magnetic drive 2,069 (300) 244 (800) 682 (3,000) 597 (800)
pump
Note: Customary Values in Parenthesis (PSIA), (FT), (GPM), (HP)
Fig 2.4.1 Dynamic pump principle
36