Page 330 - T. Anderson-Fracture Mechanics - Fundamentals and Applns.-CRC (2005)
P. 330
1656_C007.fm Page 310 Monday, May 23, 2005 5:54 PM
310 Fracture Mechanics: Fundamentals and Applications
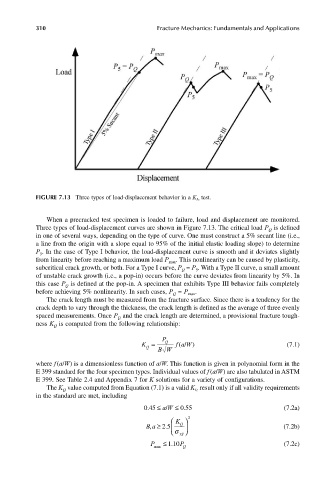
FIGURE 7.13 Three types of load-displacement behavior in a K Ic test.
When a precracked test specimen is loaded to failure, load and displacement are monitored.
Three types of load-displacement curves are shown in Figure 7.13. The critical load P is defined
Q
in one of several ways, depending on the type of curve. One must construct a 5% secant line (i.e.,
a line from the origin with a slope equal to 95% of the initial elastic loading slope) to determine
P . In the case of Type I behavior, the load-displacement curve is smooth and it deviates slightly
5
from linearity before reaching a maximum load P max . This nonlinearity can be caused by plasticity,
subcritical crack growth, or both. For a Type I curve, P = P . With a Type II curve, a small amount
Q
5
of unstable crack growth (i.e., a pop-in) occurs before the curve deviates from linearity by 5%. In
this case P is defined at the pop-in. A specimen that exhibits Type III behavior fails completely
Q
before achieving 5% nonlinearity. In such cases, P = P max .
Q
The crack length must be measured from the fracture surface. Since there is a tendency for the
crack depth to vary through the thickness, the crack length is defined as the average of three evenly
spaced measurements. Once P and the crack length are determined, a provisional fracture tough-
Q
ness K is computed from the following relationship:
Q
P
Q
K = BW fa W) (7.1)
(/
Q
where f (a/W) is a dimensionless function of a/W. This function is given in polynomial form in the
E 399 standard for the four specimen types. Individual values of f (a/W) are also tabulated in ASTM
E 399. See Table 2.4 and Appendix 7 for K solutions for a variety of configurations.
The K value computed from Equation (7.1) is a valid K result only if all validity requirements
Q
Ic
in the standard are met, including
045 ≤ . / aW ≤ 055 (7.2a)
.
K 2
Q
,
Ba ≥ 25 σ YS (7.2b)
.
P ≤ . 110 P (7.2c)
max Q