Page 346 - T. Anderson-Fracture Mechanics - Fundamentals and Applns.-CRC (2005)
P. 346
1656_C007.fm Page 326 Monday, May 23, 2005 5:54 PM
326 Fracture Mechanics: Fundamentals and Applications
The sensitivity of J values to specimen size has not been fully quantified. Consequently, ASTM
u
warns that such values may be size dependent.
7.5 CTOD TESTING
The first CTOD test standard was published in Great Britain in 1979 [19]. Several years later,
ASTM published E 1290, an American version of the CTOD standard. ASTM E 1290 has been
revised several times, and the most recent version (as of this writing) was published in 2002 [20].
The original British CTOD test standard has been superceded by BS 7448 [10], which combines
K, J, and CTOD testing into a single standard. ASTM E 1820 [4] also combined these three crack-
tip parameters into a single testing standard, but E 1290 is still maintained by the ASTM Committee
E08 on Fatigue and Fracture. The CTOD test methods in E 1290 and E 1820 are similar, but the
latter standard includes provisions for generating a CTOD resistance curve. The discussion in this
section focuses primarily on the ASTM E 1820 test method.
ASTM E 1820 includes both a basic and resistance curve procedure for CTOD, much like the
J test methodology in this standard. The test method in E 1290 is comparable to the basic procedure.
The basic procedure, where stable crack growth is not considered in the analysis, is described next.
This is followed by a description of the CTOD resistance curve procedure.
Experimental CTOD estimates are made by separating the CTOD into elastic and plastic
components, similar to J tests. The elastic CTOD is obtained from the elastic K:
2
2
(
δ = K 1 − ν ) (7.20)
el
2 σ E
YS
The elastic K is related to applied load through Equation (7.4). The above relationship assumes
that d = 0.5 for linear elastic conditions (Equation (3.48)). The plastic component of CTOD is
n
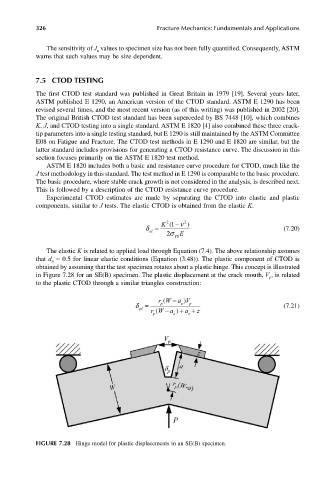
obtained by assuming that the test specimen rotates about a plastic hinge. This concept is illustrated
in Figure 7.28 for an SE(B) specimen. The plastic displacement at the crack mouth, V , is related
p
to the plastic CTOD through a similar triangles construction:
rW − a V
)
(
δ = p o p (7.21)
pl
rW − ( a + o a + ) o z
p
FIGURE 7.28 Hinge model for plastic displacements in an SE(B) specimen.