Page 391 - T. Anderson-Fracture Mechanics - Fundamentals and Applns.-CRC (2005)
P. 391
1656_C008.fm Page 371 Monday, May 23, 2005 5:59 PM
Fracture Testing of Nonmetals 371
R
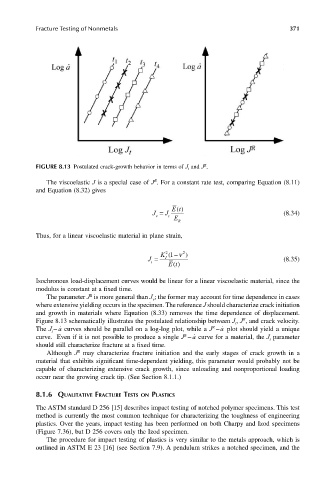
FIGURE 8.13 Postulated crack-growth behavior in terms of J t and J .
R
The viscoelastic J is a special case of J . For a constant rate test, comparing Equation (8.11)
and Equation (8.32) gives
J v J = t Et() (8.34)
E
R
Thus, for a linear viscoelastic material in plane strain,
2
K 1( −ν 2 )
J = I (8.35)
t
Et ()
Isochronous load-displacement curves would be linear for a linear viscoelastic material, since the
modulus is constant at a fixed time.
R
The parameter J is more general than J ; the former may account for time dependence in cases
v
where extensive yielding occurs in the specimen. The reference J should characterize crack initiation
and growth in materials where Equation (8.33) removes the time dependence of displacement.
R
Figure 8.13 schematically illustrates the postulated relationship between J , J , and crack velocity.
t
˙ a
˙ a
R
The J − curves should be parallel on a log-log plot, while a J − plot should yield a unique
t
˙ a
R
curve. Even if it is not possible to produce a single J − curve for a material, the J parameter
t
should still characterize fracture at a fixed time.
R
Although J may characterize fracture initiation and the early stages of crack growth in a
material that exhibits significant time-dependent yielding, this parameter would probably not be
capable of characterizing extensive crack growth, since unloading and nonproportional loading
occur near the growing crack tip. (See Section 8.1.1.)
8.1.6 QUALITATIVE FRACTURE TESTS ON PLASTICS
The ASTM standard D 256 [15] describes impact testing of notched polymer specimens. This test
method is currently the most common technique for characterizing the toughness of engineering
plastics. Over the years, impact testing has been performed on both Charpy and Izod specimens
(Figure 7.36), but D 256 covers only the Izod specimen.
The procedure for impact testing of plastics is very similar to the metals approach, which is
outlined in ASTM E 23 [16] (see Section 7.9). A pendulum strikes a notched specimen, and the