Page 131 - Fundamentals of Gas Shale Reservoirs
P. 131
DISCUSSION 111
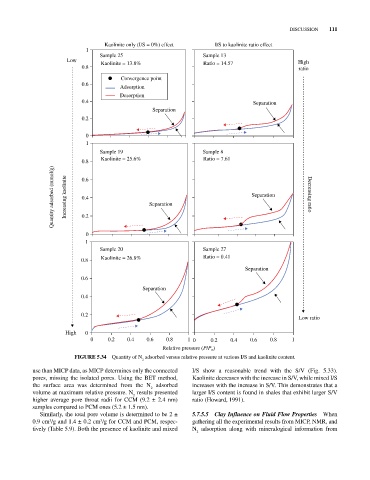
Kaolinite only (I/S = 0%) effect I/S to kaolinite ratio effect
1
Sample 25 Sample 13
Low Kaolinite = 13.8% Ratio = 14.57 High
0.8 ratio
Convergence point
0.6 Adsorption
Desorption
0.4 Separation
Separation
0.2
0
1
Sample 19 Sample 8
0.8 Kaolinite = 25.6% Ratio = 7.61
Quantity adsorbed (mmol/g) Increasing kaolinite 0.6 Separation Separation Decreasing ratio
0.4
0.2
0
1
Sample 20 Sample 27
0.8 Kaolinite = 26.8% Ratio = 0.41
Separation
0.6
Separation
0.4
0.2
Low ratio
High 0
0 0.2 0.4 0.6 0.8 1 0 0.2 0.4 0.6 0.8 1
Relative pressure (P/P )
o
FIGurE 5.34 Quantity of N adsorbed versus relative pressure at various I/S and kaolinite content.
2
use than MICP data, as MICP determines only the connected I/S show a reasonable trend with the S/V (Fig. 5.33).
pores, missing the isolated pores. Using the BET method, Kaolinite decreases with the increase in S/V, while mixed I/S
the surface area was determined from the N adsorbed increases with the increase in S/V. This demonstrates that a
2
volume at maximum relative pressure. N results presented larger I/S content is found in shales that exhibit larger S/V
2
higher average pore throat radii for CCM (9.2 ± 2.4 nm) ratio (Howard, 1991).
samples compared to PCM ones (5.2 ± 1.5 nm).
Similarly, the total pore volume is determined to be 2 ± 5.7.5.5 Clay Influence on Fluid Flow Properties When
0.9 cm /g and 1.4 ± 0.2 cm /g for CCM and PCM, respec gathering all the experimental results from MICP, NMR, and
3
3
tively (Table 5.9). Both the presence of kaolinite and mixed N adsorption along with mineralogical information from
2