Page 220 - Fundamentals of Water Treatment Unit Processes : Physical, Chemical, and Biological
P. 220
Flotation 175
(continued)
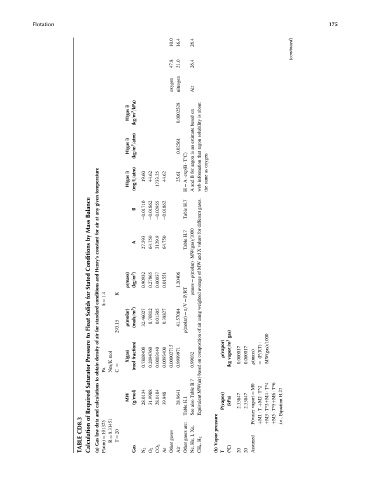
10.0 16.4 26.4
47.8 21.0 26.4
oxygen nitrogen Air
i) about
H(gas (kg=m 3 =kPa) 0.0002528 on based is
i) estimate solubility
H(gas (kg=m 3 =atm) 0.02561 an is argon argon that oxygen
temperature i) H(gas (mg=L=atm) 19.60 44.62 1733.25 44.62 25.61 H ¼ A exp(B T8C) for B and A information web as same the
Balance given any B 0.01710 0.01862 0.02955 0.01862 H.7 Table
Mass at air for
by constant A 27.593 64.750 3129.9 64.750 H.7 Table
Conditions Henry’s rmass ¼ r(molar) MW(gas)=1000
Stated and r(mass) (kg=m 3 ) 0.90932 0.27865 0.00037 0.01551 1.20406
for conditions k ¼ 1.4 K
Solids standard r(molar) ¼ n=V ¼ P=RT Equivalent MW(air) based on composition of air using weighted average of MW and X values for different gases.
Float for 293.15 r(molar) (mols=m 3 ) 32.46027 8.70812 0.01305 0.38827 41.57084
to air of gas)
Pressure density mol X(gas) fraction) 0.7808400 0.2094760 0.0003140 0.0093400 0.00002715 0.9999971 0.99032 r(vapor) vapor=m 3 0.000017 0.000017 r(mass) (P=RT) ¼ MW(gas)=1000
Saturator obtain to Pa Nm=K ¼ C (mol B.7 (kg
Required calculations and MW (g=mol) 28.0134 31.9988 28.0104 39.948 28.9641 H.1 Table Table also See P(vapor) (kPa) 2.33847 2.33847 vapor) ¼ M0 þM2 T^2 þM3 T^3þM4 T^4 þM5 T^5þM6 T^6 H.27 Equation
CD8.3 of data law R ¼ 8.31451 are: Xe, pressure P(water þM1 T i.e.,
TABLE Calculation Gas (a) P(atm) ¼ 101325 T ¼ 20 Gas N 2 O 2 CO 2 Ar gases Other Air gases Other I, He, Ne, CH 4 ,H 2 Vapor (b) T (8C) 20 20 Assumed