Page 589 - Fundamentals of Water Treatment Unit Processes : Physical, Chemical, and Biological
P. 589
544 Fundamentals of Water Treatment Unit Processes: Physical, Chemical, and Biological
Membrane
TABLE 17.3
Backing material
Organic Membrane Materials and Types Screen filter Selective
layer
of Membranes Where Used
Reverse Membrane Microporous
Microporous support
Material Microfiltration Ultrafiltration Osmosis Asymmetric
Cellulosic polymers
Cellulose acetate (CA) X X X
Cellulose triacetate X X X
Isotropic Anisotropic Isotropic Anisotropic
CA=triacetate blend X
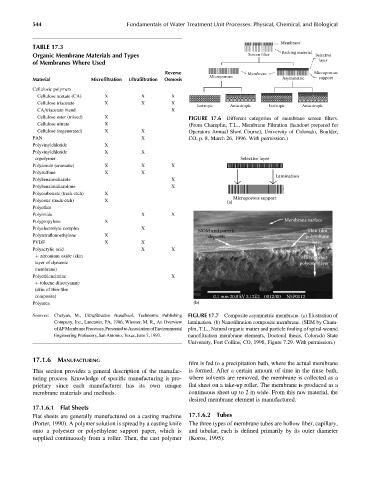
Cellulose ester (mixed) X FIGURE 17.6 Different categories of membrane screen filters.
Cellulose nitrate X (From Champlin, T.L., Membrane Filtration (handout prepared for
Cellulose (regenerated) X X Operators Annual Short Course), University of Colorado, Boulder,
PAN X CO, p. 8, March 26, 1996. With permission.)
Polyvinylchloride X
Polyvinylchloride X X
copolymer Selective layer
Polyamide (aromatic) X X X
Polysulfone X X
Lamination
Polybenzimidiazole X
Polybenzimidiazolone X
Polycarbonate (track-etch) X
Microporous support
Polyester (track-etch) X (a)
Polyether
Polyimide X X
Polypropylene X Membrane surface
Polyelectrolyte complex X
NOM and particle Thin-film
Polytetraflouoethylene X deposits polysulfone
PVDF X X layer
Polyacrylic acid X X
þ zirconium oxide (skin Microporous
layer of dynamic polyester layer
membrane)
Polyethleneimine X
þ toluene diisocyanate
(skin of thin-film
composite) 0.1 mm 20.0 kV 3.12E2 0012/00 N5P0112
Polyurea (b)
Sources: Cheryan, M., Ultrafiltration Handbook, Technomic Publishing FIGURE 17.7 Composite asymmetric membrane. (a) Illustration of
Company, Inc., Lancaster, PA, 1986; Wiesner, M. R., An Overview lamination. (b) Nanofiltration composite membrane. (SEM by Cham-
ofDPMembraneProcesses,PresentedtoAssociationofEnvironmental plin, T.L., Natural organic matter and particle fouling of spiral-wound
Engineering Professors, San Antonio, Texas, June 7, 1993. nanofiltration membrane elements, Doctoral thesis, Colorado State
University, Fort Collins, CO, 1998, Figure 7.29. With permission.)
17.1.6 MANUFACTURING
film is fed to a precipitation bath, where the actual membrane
This section provides a general description of the manufac- is formed. After a certain amount of time in the rinse bath,
turing process. Knowledge of specific manufacturing is pro- where solvents are removed, the membrane is collected as a
prietary since each manufacturer has its own unique flat sheet on a take-up roller. The membrane is produced as a
membrane materials and methods. continuous sheet up to 2 m wide. From this raw material, the
desired membrane element is manufactured.
17.1.6.1 Flat Sheets
Flat sheets are generally manufactured on a casting machine 17.1.6.2 Tubes
(Porter, 1990). A polymer solution is spread by a casting knife The three types of membrane tubes are hollow fiber, capillary,
onto a polyester or polyethylene support paper, which is and tubular; each is defined primarily by its outer diameter
supplied continuously from a roller. Then, the cast polymer (Koros, 1995):