Page 159 - Gas Purification 5E
P. 159
Alhnolamines for Hydrogen Sulfide and Carbon Dioxide Removal 147
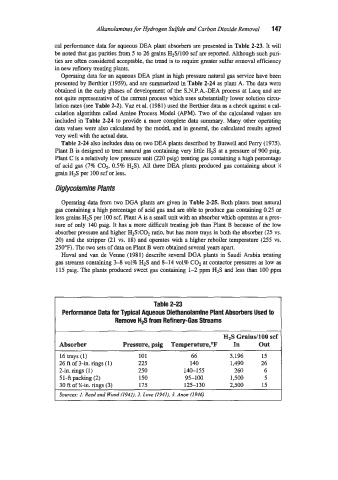
cal performance data for aqueous DEA plant absorbers are presented in Table 2-23. It will
be noted that gas purities from 5 to 26 grains H2S/100 scf are reported. Although such puri-
ties are often considered acceptable, the trend is to require greater sulfur removal efficiency
in new refinery treating plants.
Operating data for an aqueous DEA plant in high pressure natural gas service have been
presented by Berthier (1959), and are summarized in Table 2-24 as plant A. The data were
obtained in the early phases of development of the S.N.P.A.-DEA process at Lacq and are
not quite representative of the current process which uses substantially lower solution circu-
lation rates (see Table 2-2). Vaz et al. (1981) used the Berthier data as a check against a cal-
culation algorithm called Amine Process Model (APM). Two of the calculated values are
included in Table 2-24 to provide a more complete data summary. Many other operating
data values were also calculated by the model, and in general, the calculated results agreed
very well with the actual data.
Table 2-24 also includes data on two DEA plants described by Butwell and Perry (1975).
Plant B is designed to hat natural gas containing very little H2S at a pressure of 900 psig.
Plant C is a relatively low pre.ssure unit (220 psig) treating gas containing a high percentage
of zcid gas (79 COz, 0.5% H2S). All three DEA plants produced gas containing about !4
grain H,S per 100 scf or less.
Diglycolamine Plants
Operating data from two DGA plants are given in Table 2-25. Both plants treat natural
gas containing a high percentage of acid gas and are able to produce gas containing 0.25 or
less grains H,S per 100 scf. Plant A is a small unit with an absorber which operates at a pres-
sure of only 140 psig. It has a more difficult treating job than Plant B because of the low
absorber pressure and higher H2S:C02 ratio, but has more trays in both the absorber (25 vs.
20) and the stripper (21 vs. 18) and operates with a higher reboiler temperature (255 vs.
250°F). The two sets of data on Plant B were obtained several years apart.
Huval and van de Verne (1981) describe several DGA plants in Saudi Arabia treating
gas streams containing 3-8 ~01% H2S and 8-14 v018 C02 at contactor pressures as low as
115 psig. The plants produced sweet gas containing 1-2 ppm H2S and less than 100 ppm
Table 2-23
Performance Data for Typical Aqueous Diethanolamine Plant Absorbers Used to
Remove H# from Refinery-Gas Streams
~~ ~ ~ ~ ~
H2S Grains1100 scf
Absorber Pressure, psig Temperature,OF In out
16 trays (1) 101 66 3.196 15
26 ft of 3-in. rings (1) 225 140 1,490 26
2-in. rings (1) 250 140-155 260 6
5 1 -ft packing (2) 150 95-100 1,500 5
30 ft of %-in. rings (3) 175 125-130 2,500 15
Sources: 1. Reed and Wood f1941). 2. Love (1941). 3. Anon f1946)