Page 135 - Handbook of Civil Engineering Calculations, Second Edition
P. 135
1.118 STRUCTURAL STEEL ENGINEERING AND DESIGN
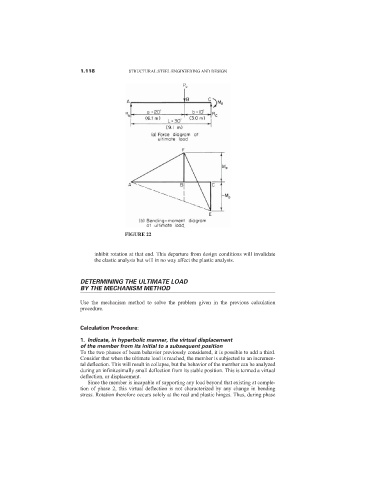
FIGURE 22
inhibit rotation at that end. This departure from design conditions will invalidate
the elastic analysis but will in no way affect the plastic analysis.
DETERMINING THE ULTIMATE LOAD
BY THE MECHANISM METHOD
Use the mechanism method to solve the problem given in the previous calculation
procedure.
Calculation Procedure:
1. Indicate, in hyperbolic manner, the virtual displacement
of the member from its initial to a subsequent position
To the two phases of beam behavior previously considered, it is possible to add a third.
Consider that when the ultimate load is reached, the member is subjected to an incremen-
tal deflection. This will result in collapse, but the behavior of the member can be analyzed
during an infinitesimally small deflection from its stable position. This is termed a virtual
deflection, or displacement.
Since the member is incapable of supporting any load beyond that existing at comple-
tion of phase 2, this virtual deflection is not characterized by any change in bending
stress. Rotation therefore occurs solely at the real and plastic hinges. Thus, during phase