Page 295 - Handbook of Lasers
P. 295
1.5.10 Quantum Cascade and Intersubband Lasers
Interband-based cascade lasers (ICL), intersubband-based quantum cascade lasers (QCL),
and non-cascaded intersubband lasers are included in this section. In the first, every injected
electron generates multiple photons by making interband transitions at each step of the
staircase-like quantum well structure; in the second an electron makes transitions between
conduction subbands created by quantum confinement. A further distinction is that quantum
cascade lasers are electrically pumped whereas quantum fountain lasers are optically pumped.
In all cases the wavelength is determined by the layer thickness of the active region rather
than the band gap, hence the lasers can be tailored to operate over a broad range of
wavelengths in the mid-infrared.
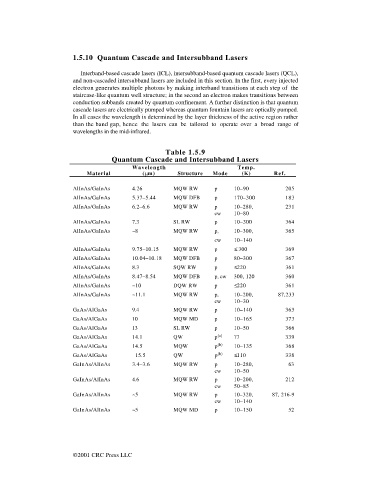
Table 1.5.9
Quantum Cascade and Intersubband Lasers
Wavelength Temp.
Material ( m) Structure Mode (K) Ref.
AlInAs/GaInAs 4.26 MQW RW p 10–90 205
AlInAs/GaInAs 5.37–5.44 MQW DFB p 170–300 183
AlInAs/GaInAs 6.2–6.6 MQW RW p 10–280, 231
cw 10–80
AlInAs/GaInAs 7.3 SL RW p 10–300 364
AlInAs/GaInAs ~8 MQW RW p, 10–300, 365
cw 10–140
AlInAs/GaInAs 9.75–10.15 MQW RW p £ 300 369
AlInAs/GaInAs 10.04–10.18 MQW DFB p 80–300 367
AlInAs/GaInAs 8.3 SQW RW p £220 361
AlInAs/GaInAs 8.47–8.54 MQW DFB p, cw 300, 120 360
AlInAs/GaInAs ~10 DQW RW p £220 361
AlInAs/GaInAs ~11.1 MQW RW p, 10–200, 87,233
cw 10–30
GaAs/AlGaAs 9.4 MQW RW p 10–140 363
GaAs/AlGaAs 10 MQW MD p 10–165 373
GaAs/AlGaAs 13 SL RW p 10–50 366
GaAs/AlGaAs 14.1 QW p (a) 77 339
GaAs/AlGaAs 14.5 MQW p (b) 10–135 368
GaAs/AlGaAs »15.5 QW p (b) £110 338
GaInAs/AlInAs 3.4–3.6 MQW RW p 10–280, 63
cw 10–50
GaInAs/AlInAs 4.6 MQW RW p 10–200, 212
cw 50–85
GaInAs/AlInAs ~5 MQW RW p 10–320, 87, 216-9
cw 10–140
GaInAs/AlInAs ~5 MQW MD p 10–150 52
©2001 CRC Press LLC