Page 294 - Handbook of Lasers
P. 294
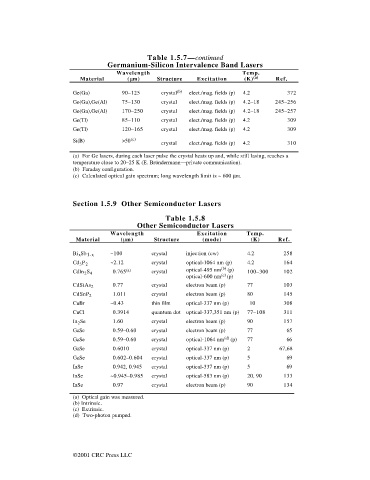
Table 1.5.7— continued
Germanium-Silicon Intervalence Band Lasers
Wavelength Temp.
(a)
Material ( m) Structure Excitation (K) Ref.
Ge(Ga) 90–125 crystal (b) elect./mag. fields (p) 4.2 372
Ge(Ga),Ge(Al) 75–130 crystal elect./mag. fields (p) 4.2–18 245–256
Ge(Ga),Ge(Al) 170–250 crystal elect./mag. fields (p) 4.2–18 245–257
Ge(Tl) 85–110 crystal elect./mag. fields (p) 4.2 309
Ge(Tl) 120–165 crystal elect./mag. fields (p) 4.2 309
Si(B) >50 (c) crystal elect./mag. fields (p) 4.2 310
(a) For Ge lasers, during each laser pulse the crystal heats up and, while still lasing, reaches a
temperature close to 20–25 K (E. Bründermann—private communication).
(b) Faraday configuration.
(c) Calculated optical gain spectrum; long wavelength limit is ~ 600 mm.
Section 1.5.9 Other Semiconductor Lasers
Table 1.5.8
Other Semiconductor Lasers
Wavelength Excitation Temp.
Material ( m) Structure (mode) (K) Ref.
Bi Sb 1-x ~100 crystal injection (cw) 4.2 258
x
Cd P ~2.12 crystal optical-1064 nm (p) 4.2 164
3 2
(b)
CdIn S 0.765 (a) crystal optical-495 nm (p) 100–300 102
2 4
(c)
optical-600 nm (p)
CdSiAs 2 0.77 crystal electron beam (p) 77 103
CdSnP 2 1.011 crystal electron beam (p) 80 145
CuBr ~0.43 thin film optical-337 nm (p) 10 308
CuCl 0.3914 quantum dot optical-337,351 nm (p) 77–108 311
In Se 1.60 crystal electron beam (p) 90 157
2
GaSe 0.59–0.60 crystal electron beam (p) 77 65
(d)
GaSe 0.59–0.60 crystal optical-1064 nm (p) 77 66
GaSe 0.6010 crystal optical-337 nm (p) 2 67,68
GaSe 0.602–0.604 crystal optical-337 nm (p) 5 69
InSe 0.942, 0.945 crystal optical-337 nm (p) 5 69
InSe ~0.945–0.985 crystal optical-583 nm (p) 20, 90 133
InSe 0.97 crystal electron beam (p) 90 134
(a) Optical gain was measured.
(b) Intrinsic.
(c) Extrinsic.
(d) Two-photon pumped.
©2001 CRC Press LLC