Page 48 - Handbook of Materials Failure Analysis
P. 48
3 Case Studies 41
3.2.3 Description of Process
The detail of any chemical addition in CT water and information regarding opera-
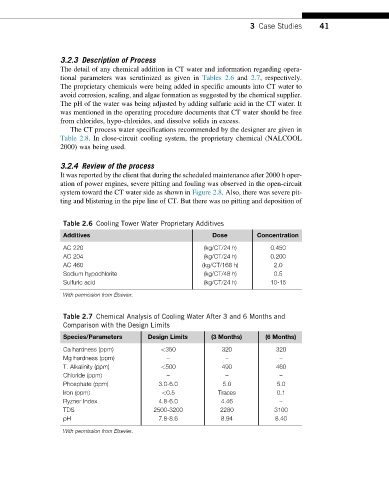
tional parameters was scrutinized as given in Tables 2.6 and 2.7, respectively.
The proprietary chemicals were being added in specific amounts into CT water to
avoid corrosion, scaling, and algae formation as suggested by the chemical supplier.
The pH of the water was being adjusted by adding sulfuric acid in the CT water. It
was mentioned in the operating procedure documents that CT water should be free
from chlorides, hypo-chlorides, and dissolve solids in excess.
The CT process water specifications recommended by the designer are given in
Table 2.8. In close-circuit cooling system, the proprietary chemical (NALCOOL
2000) was being used.
3.2.4 Review of the process
It was reported by the client that during the scheduled maintenance after 2000 h oper-
ation of power engines, severe pitting and fouling was observed in the open-circuit
system toward the CT water side as shown in Figure 2.8. Also, there was severe pit-
ting and blistering in the pipe line of CT. But there was no pitting and deposition of
Table 2.6 Cooling Tower Water Proprietary Additives
Additives Dose Concentration
AC 220 (kg/CT/24 h) 0.450
AC 204 (kg/CT/24 h) 0.200
AC 460 (kg/CT/168 h) 2.0
Sodium hypochlorite (kg/CT/48 h) 0.5
Sulfuric acid (kg/CT/24 h) 10-15
With permission from Elsevier.
Table 2.7 Chemical Analysis of Cooling Water After 3 and 6 Months and
Comparison with the Design Limits
Species/Parameters Design Limits (3 Months) (6 Months)
Ca hardness (ppm) <350 320 320
Mg hardness (ppm) – – –
T. Alkalinity (ppm) <500 490 460
Chloride (ppm) – – –
Phosphate (ppm) 3.0-6.0 5.0 5.0
Iron (ppm) <0.5 Traces 0.1
Ryzner Index 4.8-6.0 4.46 –
TDS 2500-3200 2280 3100
pH 7.8-8.6 8.94 8.40
With permission from Elsevier.