Page 34 - Handbook of Surface Improvement and Modification
P. 34
2.2 Additives used 29
2.2.13 ZIRCONIUM PHOSPHATE AND OXIDE
GENERAL INFORMATION
Name: zirconium phosphate and zirconium oxide Active ingredient, wt%: 98
CAS #: 13765-95-2; 1314-23-4 EC #: 237-375-7; 234-843-2
PHYSICAL PROPERTIES
State: powder Odor: odorless Color: white
2
o
o
Melting point, C: 2715 Boiling point, C: 4300 Specific surface area, m /g: 70
3
Density, kg/m : 3300-5680 Particle size, nm: 50 Refractive index: 2.13
HEALTH & SAFETY
o
o
Autoignition, C: >1000 Flash point, C: non-flammable Mouse LD50, mg/kg: >8800
3
OSHA, PEL, mg/m : 5 Carcinogenic: no
Scratch-resistant, transparent coat-
ings were obtained using non-
hydrolytic sol-gel containing ZrO 2
nanoparticles in epoxy resin. 44
ZrO nanoparticles had a crystal-
2
line structure attributable to a tet-
ragonal phase and an average
44
particle size of 2 nm. The coat-
ings containing 5 and 10 wt% zir-
conia had a good adhesion and a
negligible effect on the transpar-
44
ency of coating. An increased
scratch-resistance was obtained by
increasing the ZrO nanoparticles
2
44
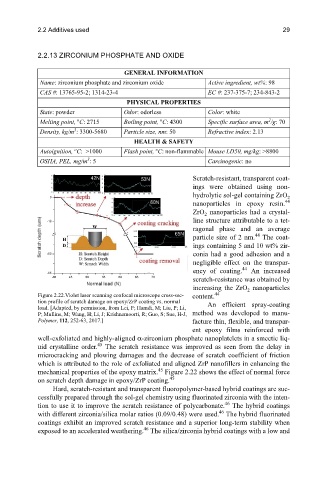
Figure 2.22.Violet laser scanning confocal microscope cross-sec- content.
tion profile of scratch damage on epoxy/ZrP coating vs. normal An efficient spray-coating
load. [Adapted, by permission, from Lei, F; Hamdi, M; Liu, P; Li,
P; Mullins, M; Wang, H; Li, J; Krishnamoorti, R; Guo, S; Sue, H-J, method was developed to manu-
Polymer, 112, 252-63, 2017.] facture thin, flexible, and transpar-
ent epoxy films reinforced with
well-exfoliated and highly-aligned α-zirconium phosphate nanoplatelets in a smectic liq-
45
uid crystalline order. The scratch resistance was improved as seen from the delay in
microcracking and plowing damages and the decrease of scratch coefficient of friction
which is attributed to the role of exfoliated and aligned ZrP nanofillers in enhancing the
45
mechanical properties of the epoxy matrix. Figure 2.22 shows the effect of normal force
45
on scratch depth damage in epoxy/ZrP coating.
Hard, scratch-resistant and transparent fluoropolymer-based hybrid coatings are suc-
cessfully prepared through the sol-gel chemistry using fluorinated zirconia with the inten-
46
tion to use it to improve the scratch resistance of polycarbonate. The hybrid coatings
46
with different zirconia/silica molar ratios (0.09/0.48) were used. The hybrid fluorinated
coatings exhibit an improved scratch resistance and a superior long-term stability when
46
exposed to an accelerated weathering. The silica/zirconia hybrid coatings with a low and