Page 277 - Hydrogeology Principles and Practice
P. 277
HYDC07 12/5/05 5:32 PM Page 260
260 Chapter Seven
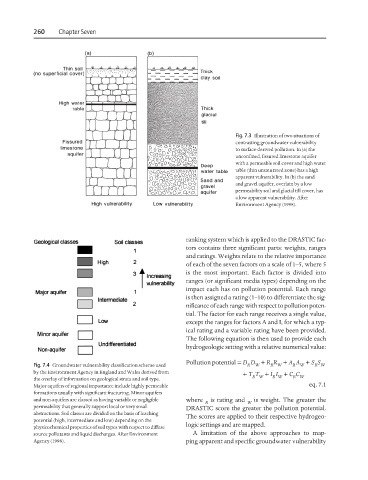
Fig. 7.3 Illustration of two situations of
contrasting groundwater vulnerability
to surface-derived pollution. In (a) the
unconfined, fissured limestone aquifer
with a permeable soil cover and high water
table (thin unsaturated zone) has a high
apparent vulnerability. In (b) the sand
and gravel aquifer, overlain by a low
permeability soil and glacial till cover, has
a low apparent vulnerability. After
Environment Agency (1998).
ranking system which is applied to the DRASTIC fac-
tors contains three significant parts: weights, ranges
and ratings. Weights relate to the relative importance
of each of the seven factors on a scale of 1–5, where 5
is the most important. Each factor is divided into
ranges (or significant media types) depending on the
impact each has on pollution potential. Each range
is then assigned a rating (1–10) to differentiate the sig-
nificance of each range with respect to pollution poten-
tial. The factor for each range receives a single value,
except the ranges for factors A and I, for which a typ-
ical rating and a variable rating have been provided.
The following equation is then used to provide each
hydrogeologic setting with a relative numerical value:
Pollution potential = D D + R R + A A + S S
Fig. 7.4 Groundwater vulnerability classification scheme used R W R W R W R W
by the Environment Agency in England and Wales derived from + T T + I I + C C
the overlay of information on geological strata and soil type. R W R W R W
Major aquifers of regional importance include highly permeable eq. 7.1
formations usually with significant fracturing. Minor aquifers
and non-aquifers are classed as having variable or negligible where is rating and is weight. The greater the
R W
permeability that generally support local or very small DRASTIC score the greater the pollution potential.
abstractions. Soil classes are divided on the basis of leaching
The scores are applied to their respective hydrogeo-
potential (high, intermediate and low) depending on the
logic settings and are mapped.
physicochemical properties of soil types with respect to diffuse
source pollutants and liquid discharges. After Environment A limitation of the above approaches to map-
Agency (1998). ping apparent and specific groundwater vulnerability