Page 208 - Improving Machinery Reliability
P. 208
Machinery Reliability Audits and Reviews 179
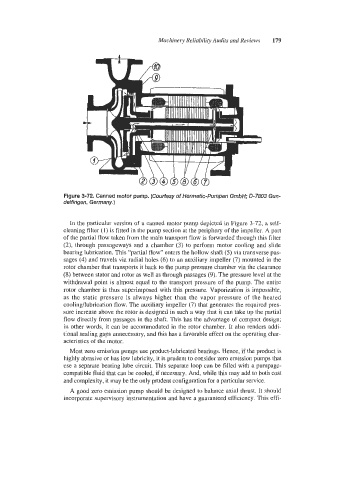
Figure 3-72. Canned motor pump. (Courtesy of Hermetic-Pumpen GmbH; 0-7803 Gun-
delfingen, Germany.)
In the particular version of a canned motor pump depicted in Figure 3-72, a self-
cleaning filter (1) is fitted in the pump section at the periphery of the impeller. A part
of the partial flow taken from the main transport flow is forwarded through this filter
(2), through passageways and a chamber (3) to perform motor cooling and slide
bearing lubrication. This “partial flow” enters the hollow shaft (5) via transverse pas-
sages (4) and travels via radial holes (6) to an auxiliary impeller (7) mounted in the
rotor chamber that transports it back to the pump pressure chamber via the clearance
(8) between stator and rotor as well as through passages (9). The pressure level a1 the
withdrawal point is almost equal to the transport pressure of the pump. The entire
rotor chamber is thus superimposed with this pressure. Vaporization is impossible,
as the static pressure is always higher than the vapor pressure of the heated
coohghbrication flow. The auxiliary impeller (7) that generates the required pres-
sure increase above the rotor is designed in such a way that it can take up the partial
flow directly from passages in the shaft. This has the advantage of compact design;
in other words, it can be accommodated in the rotor chamber. It also renders addi-
tional sealing gaps unnecessary, and this has a favorable effect on the operating char-
acteristics of the motor.
Most zero emission pumps use product-lubricated bearings. Hence, if the product is
highly abrasive or has low lubricity, it is prudent to consider zero emission pumps that
use a separate bearing lube circuit. This separate loop can be filled with a pumpage-
compatible fluid that can be cooled, if necessary. And, while this may add to both cost
and complexity, it may be the only prudent configuration for a particular service.
A good zero emission pump should be designed to balance axial thrust. It should
incorporate supervisory instrumentation and have a guaranteed efficiency. This effi-