Page 210 - Improving Machinery Reliability
P. 210
Machinery Reliability Audits and Reviews 181
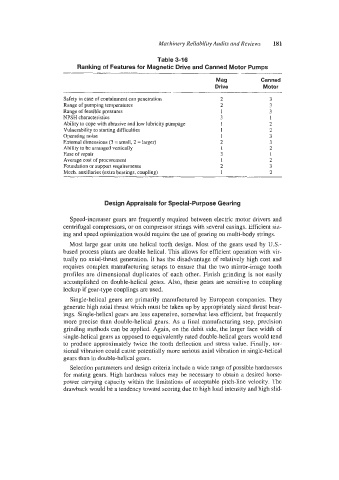
Table 3-16
Ranking of Features for Magnetic Drive and Canned Motor Pumps
Mag Canned
Drive Motor
Safety in case of containment can penetration 2 3
Range of pumping temperatures 2 3
Range of feasible pressures 1 3
NPSH characteristics 3 1
Ability to cope with abrasive and low lubricity pumpage 1 2
Vulnerability to starting difficulties 1 2
Operating noise 1 3
Ectemal dimensions (3 = small, 2 = larger) 2 3
Ability to be arranged vertically 1 2
Ease of repair 3 1
Average cost of procurement 1 2
Foundation or support requirements 2 3
Mech. auxiliaries (extra bearings, coupling) 1 2
Design Appraisals for Special-Purpose Gearing
Speed-increaser gears are frequently required between electric motor drivers and
centrifugal compressors, or on compressor strings with several casings. Efficient siz-
ing and speed optimization would require the use of gearing on multi-body strings.
Most large gear units use helical tooth design. Most of the gears used by U.S.-
based process plants are double helical. This allows for efficient operation with vir-
tually no axial-thrust generation. It has the disadvantage of relatively high cost and
requires complex manufacturing setups to ensure that the two mirror-image tooth
profiles are dimensional duplicates of each other. Finish grinding is not easily
accomplished on double-helical gears. Also, these gears are sensitive to coupling
lockup if gear-type couplings are used,
Single-helical gears are primarily manufactured by European companies. They
generate high axial thrust which must be taken up by appropriately sized thrust bear-
ings. Single-helical gears are less expensive, somewhat less efficient, but frequently
more precise than double-helical gears. As a final manufacturing step, precision
grinding methods can be applied. Again, on the debit side, the larger face width of
single-helical gears as opposed to equivalently rated double-helical gears would tend
to produce approximately twice the tooth deflection and stress value. Finally, tor-
sional vibration could cause potentially more serious axial vibration in single-helical
gears than in double-helical gears.
Selection parameters and design criteria include a wide range of possible hardnesses
for mating gears. High hardness values may be necessary to obtain a desired horse-
power carrying capacity within the limitations of acceptable pitch-line velocity. The
drawback would be a tendency toward scoring due to high load intensity and high slid-