Page 324 - Industrial Power Engineering and Applications Handbook
P. 324
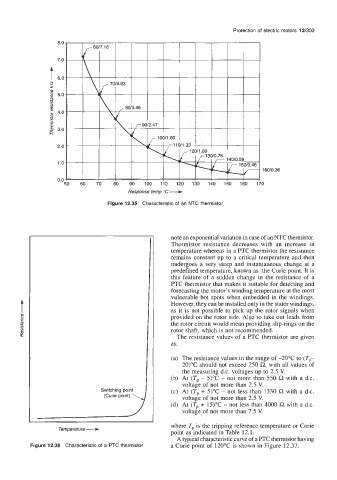
Protection of electric motors 12/303
Response temp "C - 3 160/0.36
Figure 12.35 Characteristic of an NTC thermistor
note an exponential variation in case of an NTC thermistor.
Thermistor resistance decreases with an increase in
temperature whereas in a PTC thermistor the resistance
remains constant up to a critical temperature and then
undergoes a very steep and instantaneous change at a
predefined temperature, known as the Curie point. It is
this feature of a sudden change in the resistance of a
PTC thermistor that makes it suitable for detecting and
forecasting the motor's winding temperature at the most
vulnerable hot spots when embedded in the windings.
However, they can be installed only in the stator windings,
as it is not possible to pick up the rotor signals when
provided on the rotor side. Also to take out leads from
the rotor circuit would mean providing slip-rings on the
rotor shaft, which is not recommended.
The resistance values of a PTC thermistor are given
as:
(a) The resistance values in the range of -20°C to (Tp-
20)"C should not exceed 250 0, with all values of
the measuring d.c. voltages up to 2.5 V.
(b) At (Tp - 5)"C - not more than 550 !2 with a d.c.
voltage of not more than 2.5 V.
,a
Switching point
(c) At (T,, + 3°C - not less than 1330 R with a d.c.
(Curie point) \
voltage of not more than 2.5 V.
(d) At (Tp + 15)"C - not less than 4000 R with a d.c.
voltage of not more than 7.5 V.
where Tp. is the tripping reference temperature or Curie
point as indicated in Table 12.1.
A typical characteristic curve of a PTC thermistor having
Figure 12.36 Characteristic of a PTC thermistor a Curie point of 120°C is shown in Figure 12.37.