Page 319 - Industrial Power Engineering and Applications Handbook
P. 319
12/298 Industrial Power Engineering and Applications Handbook
the cooling time effect between the two starts if it
existed, to protect the machine against excessive
stresses by a lock-out feature against repeated starts
when the summated starting time exceeds the preset
time. The total time of start is set according to the
__-- thermal capacity of the machine.
0 Likely settings - summated starting time versus tripping
time, or 8 versus tripping time.
4 Overcurrent protection. To provide a thermal replica
protection, the relay is set according to motor's heating
and cooling (I' - t) curves supplied by the motor
manufacturer. If these curves are not available, they
can be established with the help of motor heating and
I I I cooling time constants, as in equations (3.2) and (3.4).
'L i3 j A brief procedure to establish the motor thermal curves
Time-
when they are not available is explained in Section
One
cycle
3.6.
5 System unbalance protection. As discussed earlier,
During an overload condition, the relay may
be set to give alarm if normal conditions an asymmetry in the supply voltage causes
High 12R losses in the stator, and
do not restore by the end of the cycle. Thus, besides voltage unbalance it can also detect an
Eddy current losses in the rotor.
r inter-turn fault, which leads to a current unbalance. A
small amount of unbalance is already detected by the
thermal element of the overcurrent protection but a
.? severe unbalance, such as during a single phasing,
m
is
m" would require quicker protection and hence, this
2 I protection. The relay may be set for an I, of around
2 N 3% or so.
s! u?
II Likely setting: I, versus tripping time.
eel 2
$ 041 6 Short-circuit protection. To provide an instantaneous
tripping on a short-circuit delay of, say, one or two
e,, = e, cycles may be introduced into the tripping circuit to
bypass any transient currents and avoid an unwanted
Time - trip.
Likely setting: I,, versus tripping time.
0 tl t2 5 t4 7 Ground leakage current protection. A separate ground
fault protection should normally not be required in
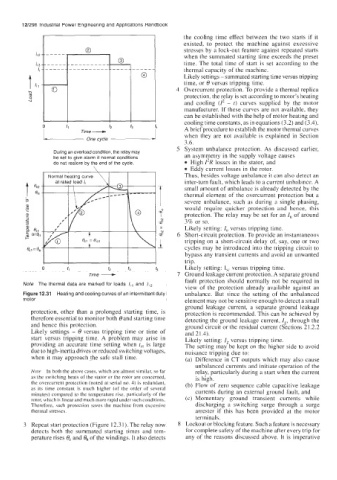
Note The thermal data are marked for loads I,, and /12
view of the protection already available against an
Figure 12.31 Heating and cooling curves of an intermittent duty unbalance. But since the setting of the unbalanced
motor element may not be sensitive enough to detect a small
ground leakage current, a separate ground leakage
protection, other than a prolonged starting time, is protection is recommended. This can be achieved by
therefore essential to monitor both 8 and starting time detecting the ground leakage current, I,, through the
and hence this protection. ground circuit or the residual current (Sections 21.2.2
Likely settings - 8 versus tripping time or time of and 2 1.4).
start versus tripping time. A problem may arise in Likely setting: Zg versus tripping time.
providing an accurate time setting when tSt is large The setting may be kept on the higher side to avoid
due to high-inertia drives or reduced switching voltages, nuisance tripping due to:
when it may approach the safe stall time. (a) Difference in CT outputs which may also cause
unbalanced currents and initiate operation of the
Nofe In both the above cases, which are almost similar, so far relay, particularly during a start when the current
as the switching heats of the stator or the rotor are concerned, is high.
the overcurrent protection (noted at serial no. 4) is redundant, (b) Flow of zero sequence cable capacitive leakage
as its time constant is much higher (of the order of several currents during an external ground fault, and
minutes) compared to the temperature rise, particnlarly of the
rotor, which is linear and much more rapid under such conditions. (c) Momentary ground transient currents while
Therefore, such protection saves the machine from excessive discharging a switching surge through a surge
thermal stresses. arrester if this has been provided at the motor
terminals.
3 Repeat start protection (Figure 12.31). The relay now 8 Lockout or blocking feature. Such a feature is necessary
detects both the summated starting times and tem- for complete safety of the machine after every trip for
perature rises 8, and 61, of the windings. It also detects any of the reasons discussed above. It is imperative