Page 555 - Industrial Power Engineering and Applications Handbook
P. 555
Captive (emergency) power generation 161529
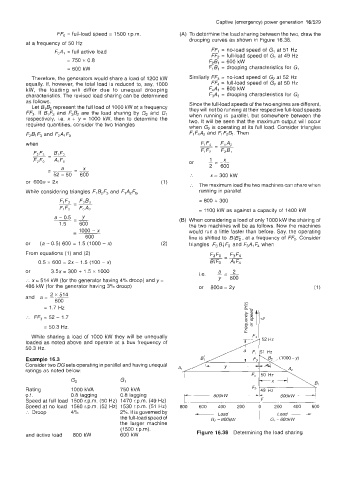
FF, = full-load speed = 1500 r.p.m. (A) To determine the load sharing between the two, draw the
drooping curves as shown in Figure 16.38.
at a frequency of 50 Hz
FoAl = full active load FF, = no-load speed of G1 at 51 Hz
FF2 = full-load speed of GI at 49 Hz
= 750 x 0.8 F2B1 = 600 kW
= 600 kW FIB, = drooping characteristics for G,
Therefore, the generators would share a load of 1200 kW Similarly FF3 = no-load speed of G2 at 52 Hz
equally. If, however, the total load is reduced to, say, 1000 Ff4 = full-load speed of Gz at 50 Hz
kW, the loading will differ due to unequal drooping F4Aj = 800 kW
characteristics. The revised load sharing can be determined F3A1 = drooping characteristics for G2
as follows. Since the full-load speeds of the two engines are different,
Let 61B2 represent the full load of 1000 kW at a frequency they will not be running at their respective full-load speeds
ff3. B,F3 and F3B2 are the load sharing by G2 and G, when running in parallel, but somewhere between the
If
respectively, i.e. x + y = 1000 kW, then to determine the
required quantities, consider the two triangles two. It will be seen that the maximum output will occur
when G2 is operating at its full load. Consider triangles
F2BiF3 and FzA1 Fo FqF4A2 and F, F2B. Then
when -- F4A2
FiF,
FzB1
-- -- F,Fz ’-
F2F3
B1F3
FZFLl AIFO or
a X 2 600
- 52-50-600 .. x = 300 kW
or 600a = 2x
:. The maximum load the two machines can share when
While considering triangles F, B2F3 and flA,Fo, running in parallel
= 800 + 300
= 1100 kW as against a capacity of 1400 kW
a-0.5- Y (B) When considering a load of only 1000 kW the sharing of
1.5 600 the two machines will be as follows. Now the machines
- 1000 - x would run a little faster than before. Say, the operating
-~
600 line is shifted to BiB;, at a frequency of FFo. Consider
or (a - 0.5) 600 = 1.5 (1000 - x) triangles F3 BiFo and 4A, F4 when
From equations (1) and (2)
0.5~600=2~-1.5(100-~)
= 300 + 1.5 x 1000
or 3.5~
i.e. - a- - 2
~
:. x = 51 4 kW (for the generator having 4% droop) and y = y 800
486 kW (for the generator having 3% droop) or 800a = 2y
2 x 514
and a= ___
600
= 1.7 HZ
... FF3 = 52 - 1.7 s
= 50.3 Hz.
While sharing a load of 1000 kW they will be unequally 52 Hz
loaded as noted above and operate at a bus frequency of
50.3 Hz.
il Hz
Example 16.3
Consider two DG sets operating in parallel and having unequal
ratings as noted below:
G2 GI -X
Rating 1000 kVA 750 kVA 19 Hz
p.f. 0.8 lagging 0.8 lagging t 600kW ~ 4
Speed at full load 1500 r.p.m. (50 Hz) 1470 r.p.m. (49 Hz) F
Speed at no load 1560 r.p.m. (52 Hz) 1530 r.p.m. (51 Hz) 800 - 200 0 200 ~ -
400
400
600
600
:. Droop 4% 2%. It is governed by Load Load
the full-load speed of G2 - 800kW I GI - 600kW
the larger machine
(1500 r.p.m).
and active load 800 kW 600 kW Figure 16.38 Determining the load sharing