Page 733 - Industrial Power Engineering and Applications Handbook
P. 733
Grounding theory and ground fault protection schemes 21/693
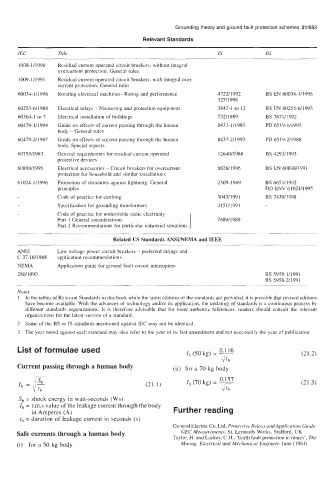
Relevant Standards
IEC Title IS BS
1008-111990 Residual current operated circuit breakers, without integral
overcurrent protection, General rules
1009- 111 99 1 Residual current operated circuit breakers, with integral over
current protection, General rules
60034-1/1996 Rotating electrical machines-Rating and performance 4722/1992 BS EN 60034-1/1995
325/1996
60255-6/1988 Electrical relays - Measuring and protection equipment 3842-1 to 12 BS EN 60255-6/1995
60364-1 to 7 Electrical installation of buildings 732/1989 BS 7671/1992
60479-111994 Guide on effects of current passing through the human 8437- 111993 PD 6519-1/1995
body - General rules
60479-2/1987 Guide on effects of current passing through the human 8437-2/1993 PD 6519-2/1988
body. Special aspects
60755/1983 General requirements for residual current operated 12640/1988 BS 4293/1993
protective devices
60898/1995 Electrical accessories - Circuit breakers for overcurrent 8828/1996 BS EN 60898/1991
protection for household and similar installations
61024- 1/1996 Protection of structures against lightning. General 2309-1989 BS 6651/1992
principles DD ENV 61024/1995
Code of practice for earthing 3043/199 1 BS 7430/1998
Specification for grounding transformers 3151/1991 -
Code of practice for undesirable static electricity
Part 1 General considerations 768911989
Part 2 Recommendations for particular industrial situations
Related US Standards ANSI/NEMA and IEEE
ANSI Low voltage power circuit breakers - preferred ratings and
C 37.16/1988 application recommendations
NEMA Application guide for ground fault circuit interrupters
280/1990 BS 5958-111991
BS 5958-2/1991
Notes
1 In the tables of Relevant Standards in this book while the latest editions of the standards are provided, it is possible that revised editions
have become available. With the advances of technology and/or its application, the updating of standards is a continuous process by
different standards organizations. It is therefore advisable that for more authentic references, readers should consult the relevant
organizations for the latest version of a standard.
2 Some of the BS or IS standards mentioned against IEC may not be identical.
3 The year noted against each standard may also refer to the year of its last amendment and not necessarily the year of publication.
List of formulae used I, (50 kg) = - (21.2)
0.116
&
Current passing through a human body (ii) for a 70 kg body
0.157
(21.1) Ib (70 kg) = - (21.3)
Sb = shock energy in watt-seconds (ws)
Ib = r.m.s value of the leakage current through the body
in Amperes (A) Further reading
tb = duration of leakage current in seconds (s)
General Electric Co. Ltd, Protective Relays and Application Guide,
Safe currents through a human body GEC Measurements, St, Leonards Works, Stafford, UK
Taylor, H. and Lackey, C.H., ‘Earth fault protection in mines’, The
(i) for a 50 kg body Mining, Electrical and Mechanical Engineec June (1961)