Page 787 - Industrial Power Engineering and Applications Handbook
P. 787
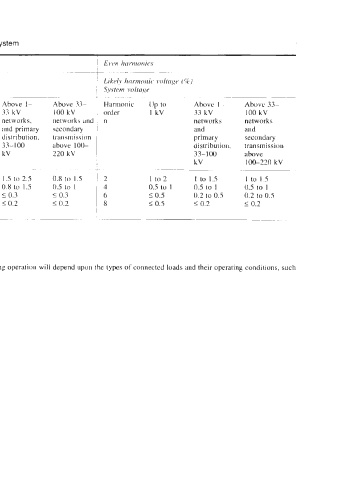
Table 23.1 Typical harmonic orders and their magnitudes as studied in a power system
Odd harmonic
-~
Likeh harmonit voltage (%J
S\ \tern voltage Syttern voltage
~ ~ ~
Harmonic up to Above 1- Above 33- Hdrmonic up to Above 1- Above 33- Harmonic Up to Above I- Above 33-
order I kV 33 kV 100 kV order I kV 33 kV 100 kV order I kV 33 kV 100 kV
n networks networks and n networks, network\ dnd n networks networks
and primary secondary and primary \econdary and and
distribution. transmission distribution, tran\mi\$ion primary secondary
33-100 above 100- 33-100 above 100- distnbution, transmission
kV 220 kV kV 220 kV 33-100 above
kV 100-220 kV
~~- ~ - ~ ~~
5 4 to 6 5 to 6 1 to 2 3 4 to 5 1.5 to 2.5 0.8 to 1.5 2 1 to 2 1 to 1.5 1 to 1.5
7 4 to 5 4 to 5 I to 2 9 0.8 to .5 0.8 to 1.5 0.5 to I 4 0.5 to 1 0.5 to 1 0.5 to I
II 2.5 to 3.5 2.5 to 3.5 0.8 to .5 15 5 0.3 5 0.3 5 0.3 6 5 0.5 0.2 to 0.5 0.2 to 0.5
13 2 to 3 2 to 3 0.8 to .5 21 5 0.2 5 0.2 5 0.2 8 5 0.5 50.2 5 0.2
17 I to 2 1 to 2 0.5 to
~~
Source lEEE 51 9, ,for general and dedicuted power systems
Notes
1 Still higher harmonics have not been conqidered, as they are of even lower magnitudes.
2 The values are expressed as a percentage of the fundamental voltage.
3 The above data is for a general reference. Actual harmonic distortion on the sybtem during operation will depend upon the types of connected loads and their operating conditions, such
as variation in its loading and fluctuations in the system voltage.