Page 353 - Instrumentation Reference Book 3E
P. 353
336 Chemical analysis: spectroscopy
technique include such problems as locating hydro- solids, liquids, and gases and has a wide range of
gen atoms in solids, measuring bond lengths, crys- application in process monitoring and laboratory
tal imperfections, and determination of crystalline research. When combined with the gas chroma-
and amorphous fractions in polymers. tograph it provides an extremely powerful tool
for identifying and quantifying substances which
may be present in extremely small quantities.
16.6 Neutron activation
While the optical spectrometer resolves a beam
of light into components according to their wave-
Gamma ray spectroscopy is the technique by lengths, a mass spectrometer resolves a beam of
which the intensities of various gamma energies positive ions into components according to their
emanating from a radioactive source are mea- masskharge ratio, or if all carry single elementary
sured. (See Chapter 23.) It can be used for quali- charges, according to their masses. As with the
tative identification of the components of optical spectrometer the mass spectrometer may
radionuclide mixtures and for quantitative deter- be used to identify substances and to measure the
mination of their relative abundance. Such a quantity present.
situation arises in neutron activation analysis. The original mass spectrometer was devised by
This is a technique of chemical analysis for extre- F. W. Aston about 1919 to measure the mass of
mely minute traces down to ppb (parts per 10’) of individual positive ions. The accuracy of the
chemical elements in a sample. It employs a beam instrument enabled the different masses of what
of neutrons for activation of isotopes which can appeared to be chemically identical atoms to be
then be identified, with counters, by the radio- measured, resulting in the discovery of isotopes.
active characteristics of the new nuclear species. Considerable development has taken place over
This technique has been applied for the trace the years, resulting in very versatile instruments
analysis of many elements in a variety of materi- having very high resolving power and sensitivity.
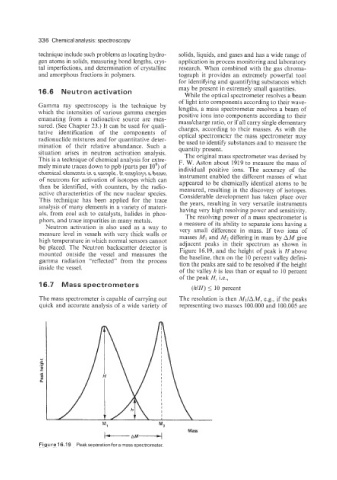
als, from coal ash to catalysts, halides in phos- The resolving power of a mass spectrometer is
phors, and trace impurities in many metals. a measure of its ability to separate ions having a
Neutron activation is also used as a way to
measure level in vessels with very thick walls or very small difference in mass. If two ions of
masses iM1 and M2 differing in mass by AM give
high temperature in which normal sensors cannot adjacent peaks in their spectrum as shown in
be placed. The Neutron backscatter detector is Figure 16.19, and the height of peak is H above
mounted outside the vessel and measures the the baseline, then on the 10 percent valley defini-
gamma radiation “reflected” from the process tion the peaks are said to be resolved if the height
inside the vessel.
of the valley h is less than or equal to 10 percent
of the peak H, i.e.,
16.7 Mass spectrometers (hlH) 5 10 percent
The mass spectrometer is capable of carrying out The resolution is then MlIAM, e.g., if the peaks
quick and accurate analysis of a wide variety of representing two masses 100.000 and 100.005 are
Figure 16.19 Peakseparationfora mass spectrometer