Page 146 - Integrated Wireless Propagation Models
P. 146
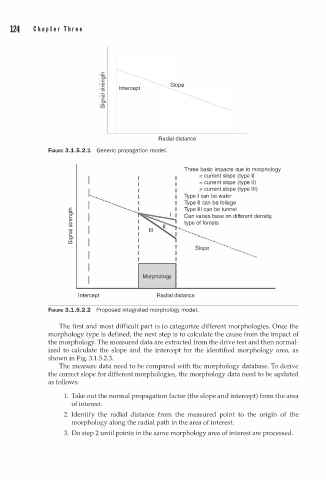
124 C h a p t e r T h r e e
In tercept Slope
Radial distance
FIGURE 3.1.5.2.1 Generic propagation mod l.
e
Three basic impacts due to morphology
< current slope (type I)
I = c urrent slope (type II)
>current slope (type )
l
l
I
Type I can be water
-·
I
I
: · · ·· ·· ······ Type can be foliage
-··
Type can be tunnel
l
l
I
.r: · ·
c, Can varies base on different density,
c
� I type of forests
1ii
Cii I .. .
c --- ----··· · ·· .. ... .
Cl ..
Ui I ::�: ; . . ·
-
I . · ....
-
I
Morphology
I
In tercept Radial distance
FIGURE 3.1.5.2.2 Proposed integrated morphology mode l.
The first and most difficult part s t o categorize different morphologies. Once the
i
morphology type is defined, the next step is to calculate the cause from the impact of
the morphology. The measured data are extracted from the drive test and then normal
ized to calculate the slope and the intercept for the identified morphology area, as
shown in Fig. 3.1.5.2.3.
The measure data need to be compared with the morphology database. To derive
the correct slope for different morphologies, the morphology data need to be updated
as follows:
1. Take out the normal propagation factor (the slope and intercept) from the area
of interest.
2. Identify the radial distance from the measured point to the origin of the
morphology along the radial path in the area of interest.
3. Do step 2 until points in the same morphology area of interest are processed.