Page 51 - Integrated Wireless Propagation Models
P. 51
I n t r o d u c t i o n t o M o d e l i n g M o b i l e S i g n a l s i n W i r e l e s s C o m m u n i c a t i o n s 29
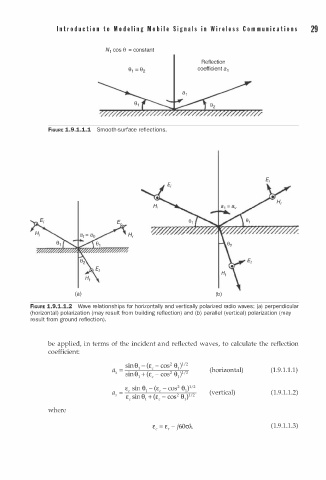
N 1 cos 9 = c onstant
Reflection
coefficient a 1
FIGURE 1.9.1.1.1 Smooth-surface reflections.
H,
(a) (b)
l
FIGURE 1.9.1.1.2 Wave relationships for horizonta l y and vertica l y polarized radio waves: (a) perpendicular
l
(horizontal) polarization (may result from building reflection) and (b) parallel (vertical) polarization (may
result from ground reflection).
be applied, in terms of the incident and reflected waves, to calculate the reflection
coefficient:
.
(horizontal) (1. 9 . 1 . 1 )
1
(vertical) (1.9. . 1 .2)
1
where
1
E = E , - j60dA (1.9. . 1 .3)
c