Page 306 - Introduction to chemical reaction engineering and kinetics
P. 306
11.2 Examples of Reactors for Illustration of Process Design Considerations 287
11.2.3.2 Fixed-Bed Catalytic Reactors: Ammonia Synthesis
The synthesis of ammonia, N2 + 3H, = 2NH,, like the oxidation of SO, (Section 1.54
and Figure 1.4) is an exothermic, reversible, catalytic reaction carried out in a multi-
stage tubular flow reactor in which each stage consists of a (fixed) bed of catalyst par-
ticles. Unlike SO, oxidation, it is a high-pressure reaction (150-350 bar, at an average
temperature of about 450°C). The usual catalyst is metallic Fe.
The reactors used can be classified in two main ways (Twigg, 1996, p. 424):
(1) by type of flow of the gas through the beds: axial, radial, or cross-flow; and
(2) by method used to control T and recover the energy of reaction: indirect cooling
with heat exchanger surface or quench cooling.
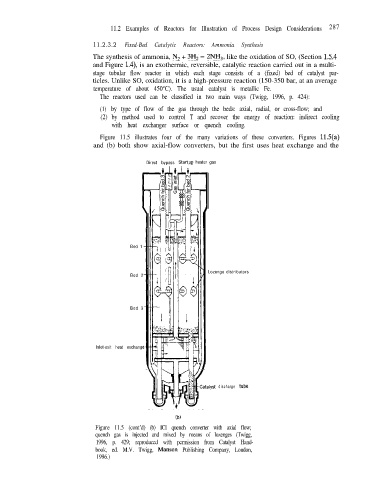
Figure 11.5 illustrates four of the many variations of these converters. Figures llS(a)
and (b) both show axial-flow converters, but the first uses heat exchange and the
Direct bypass Start .up heater gas
Bed 1
Lozenge distributors
Bed 2
Bed 3
Inlet-exit heat exchange
discharge
(b)
Figure 11.5 (cont’d) (b) ICI quench converter with axial flow;
quench gas is injected and mixed by means of lozenges (Twigg,
1996, p. 429; reproduced with permission from Catalyst Hand-
book, ed. M.V. Twigg, Manson Publishing Company, London,
1996.)