Page 386 - Sami Franssila Introduction to Microfabrication
P. 386
Moore’s Law 365
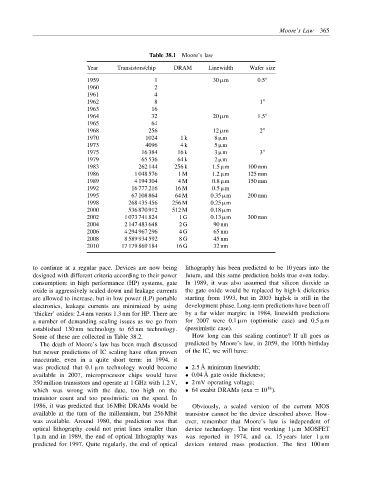
Table 38.1 Moore’s law
Year Transistors/chip DRAM Linewidth Wafer size
1959 1 30 µm 0.5 ′′
1960 2
1961 4
1962 8 1 ′′
1963 16
1964 32 20 µm 1.5 ′′
1965 64
1968 256 12 µm 2 ′′
1970 1024 1 k 8 µm
1973 4096 4 k 5 µm
1975 16 384 16 k 3 µm 3 ′′
1979 65 536 64 k 2 µm
1983 262 144 256 k 1.5 µm 100 mm
1986 1 048 576 1 M 1.2 µm 125 mm
1989 4 194 304 4 M 0.8 µm 150 mm
1992 16 777 216 16 M 0.5 µm
1995 67 108 864 64 M 0.35 µm 200 mm
1998 268 435 456 256 M 0.25 µm
2000 536 870 912 512 M 0.18 µm
2002 1 073 741 824 1 G 0.13 µm 300 mm
2004 2 147 483 648 2 G 90 nm
2006 4 294 967 296 4 G 65 nm
2008 8 589 934 592 8 G 45 nm
2010 17 179 869 184 16 G 32 nm
to continue at a regular pace. Devices are now being lithography has been predicted to be 10 years into the
designed with different criteria according to their power future, and this same prediction holds true even today.
consumption: in high performance (HP) systems, gate In 1989, it was also assumed that silicon dioxide as
oxide is aggressively scaled down and leakage currents the gate oxide would be replaced by high-k dielectrics
are allowed to increase, but in low power (LP) portable starting from 1993, but in 2003 high-k is still in the
electronics, leakage currents are minimized by using development phase. Long-term predictions have been off
‘thicker’ oxides: 2.4 nm versus 1.3 nm for HP. There are by a far wider margin: in 1984, linewidth predictions
a number of demanding scaling issues as we go from for 2007 were 0.1 µm (optimistic case) and 0.5 µm
established 130 nm technology to 65 nm technology. (pessimistic case).
Some of these are collected in Table 38.2. How long can this scaling continue? If all goes as
The death of Moore’s law has been much discussed predicted by Moore’s law, in 2059, the 100th birthday
but newer predictions of IC scaling have often proven of the IC, we will have:
inaccurate, even in a quite short term: in 1994, it
was predicted that 0.1 µm technology would become • 2.5 ˚ A minimum linewidth;
available in 2007, microprocessor chips would have • 0.04 ˚ A gate oxide thickness;
350 million transistors and operate at 1 GHz with 1.2 V, • 2 mV operating voltage;
18
which was wrong with the date, too high on the • 64 exabit DRAMs (exa = 10 ).
transistor count and too pessimistic on the speed. In
1986, it was predicted that 16 Mbit DRAMs would be Obviously, a scaled version of the current MOS
available at the turn of the millennium, but 256 Mbit transistor cannot be the device described above. How-
was available. Around 1980, the prediction was that ever, remember that Moore’s law is independent of
optical lithography could not print lines smaller than device technology. The first working 1 µm MOSFET
1 µm and in 1989, the end of optical lithography was was reported in 1974, and ca. 15 years later 1 µm
predicted for 1997. Quite regularly, the end of optical devices entered mass production. The first 100 nm