Page 388 - Sami Franssila Introduction to Microfabrication
P. 388
Moore’s Law 367
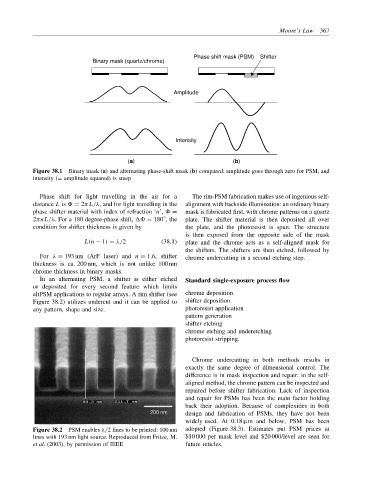
Phase shift mask (PSM) Shifter
Binary mask (quartz/chrome)
Amplitude
Intensity
(a) (b)
Figure 38.1 Binary mask (a) and alternating phase-shift mask (b) compared: amplitude goes through zero for PSM, and
intensity (= amplitude squared) is steep
Phase shift for light travelling in the air for a The rim-PSM fabrication makes use of ingenious self-
distance L is = 2πL/λ, and for light travelling in the alignment with backside illumination: an ordinary binary
phase shifter material with index of refraction ‘n’, = mask is fabricated first, with chrome patterns on a quartz
◦
2πnL/λ. For a 180 degree-phase shift, = 180 , the plate. The shifter material is then deposited all over
condition for shifter thickness is given by the plate, and the photoresist is spun. The structure
is then exposed from the opposite side of the mask
L(n − 1) = λ/2 (38.1) plate and the chrome acts as a self-aligned mask for
the shifters. The shifters are then etched, followed by
For λ = 193 nm (ArF laser) and n = 1.6, shifter chrome undercutting in a second etching step.
thickness is ca. 200 nm, which is not unlike 100 nm
chrome thickness in binary masks.
In an alternating PSM, a shifter is either etched Standard single-exposure process flow
or deposited for every second feature which limits
altPSM applications to regular arrays. A rim shifter (see chrome deposition
Figure 38.2) utilizes undercut and it can be applied to shifter deposition
any pattern, shape and size. photoresist application
pattern generation
shifter etching
chrome etching and underetching
photoresist stripping.
Chrome undercutting in both methods results in
exactly the same degree of dimensional control. The
difference is in mask inspection and repair: in the self-
aligned method, the chrome pattern can be inspected and
repaired before shifter fabrication. Lack of inspection
and repair for PSMs has been the main factor holding
back their adoption. Because of complexities in both
design and fabrication of PSMs, they have not been
widely used. At 0.18 µm and below, PSM has been
Figure 38.2 PSM enables λ/2 lines to be printed: 100 nm adopted (Figure 38.3). Estimates put PSM prices at
lines with 193 nm light source. Reproduced from Fritze, M. $10 000 per mask level and $20 000/level are seen for
et al. (2003), by permission of IEEE future reticles.