Page 59 - Sami Franssila Introduction to Microfabrication
P. 59
38 Introduction to Microfabrication
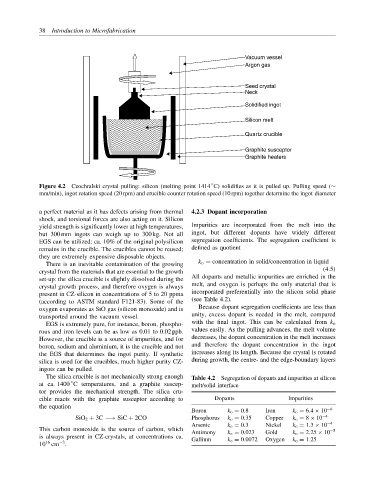
Vacuum vessel
Argon gas
Seed crystal
Neck
Solidified ingot
Silicon melt
Quartz crucible
Graphite susceptor
Graphite heaters
◦
Figure 4.2 Czochralski crystal pulling: silicon (melting point 1414 C) solidifies as it is pulled up. Pulling speed (∼
mm/min), ingot rotation speed (20 rpm) and crucible counter rotation speed (10 rpm) together determine the ingot diameter
a perfect material as it has defects arising from thermal 4.2.3 Dopant incorporation
shock, and torsional forces are also acting on it. Silicon
yield strength is significantly lower at high temperatures, Impurities are incorporated from the melt into the
but 300 mm ingots can weigh up to 300 kg. Not all ingot, but different dopants have widely different
EGS can be utilized: ca. 10% of the original polysilicon segregation coefficients. The segregation coefficient is
remains in the crucible. The crucibles cannot be reused; defined as quotient
they are extremely expensive disposable objects.
There is an inevitable contamination of the growing k o = concentration in solid/concentration in liquid
crystal from the materials that are essential to the growth (4.5)
set-up: the silica crucible is slightly dissolved during the All dopants and metallic impurities are enriched in the
crystal growth process, and therefore oxygen is always melt, and oxygen is perhaps the only material that is
present in CZ-silicon in concentrations of 5 to 20 ppma incorporated preferentially into the silicon solid phase
(according to ASTM standard F121-83). Some of the (see Table 4.2).
Because dopant segregation coefficients are less than
oxygen evaporates as SiO gas (silicon monoxide) and is
transported around the vacuum vessel. unity, excess dopant is needed in the melt, compared
EGS is extremely pure, for instance, boron, phospho- with the final ingot. This can be calculated from k o
rous and iron levels can be as low as 0.01 to 0.02 ppb. values easily. As the pulling advances, the melt volume
However, the crucible is a source of impurities, and for decreases, the dopant concentration in the melt increases
boron, sodium and aluminium, it is the crucible and not and therefore the dopant concentration in the ingot
the EGS that determines the ingot purity. If synthetic increases along its length. Because the crystal is rotated
silica is used for the crucibles, much higher purity CZ- during growth, the centre- and the edge-boundary layers
ingots can be pulled.
The silica crucible is not mechanically strong enough Table 4.2 Segregation of dopants and impurities at silicon
at ca. 1400 C temperatures, and a graphite suscep- melt/solid interface
◦
tor provides the mechanical strength. The silica cru-
cible reacts with the graphite susceptor according to Dopants Impurities
the equation
Boron k o = 0.8 Iron k o = 6.4 × 10 −6
SiO 2 + 3C −→ SiC + 2CO Phosphorus k o = 0.35 Copper k o = 8 × 10 −4
Arsenic k o = 0.3 Nickel k o = 1.3 × 10 −4
This carbon monoxide is the source of carbon, which −5
Antimony k o = 0.023 Gold k o = 2.25 × 10
is always present in CZ-crystals, at concentrations ca. Gallium k o = 0.0072 Oxygen k o = 1.25
−3
16
10 cm .