Page 187 - Lean six sigma demystified
P. 187
166 Lean Six Sigma DemystifieD
Fulfillment errors
30
25
UCL 19.84
20
UCL
+2 Sigma
+1 Sigma
Errors 15 Average
–1 Sigma
–2 Sigma
CL 10.24 LCL
10
7.05
5
2.40
L C L 6 . 0 4
0
2000–10 2000–12 2001–02 2001–04 2001–06 2001–08 2001–10 2001–12 2002–02 2002–04 2002–06 2002–08 2002–10 2002–11 2003–01 2003–03
2000-2003
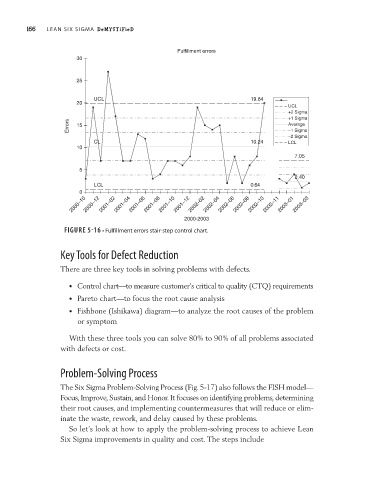
FIGURE 5-16 • Fulfillment errors stair-step control chart.
Key Tools for Defect Reduction
There are three key tools in solving problems with defects.
• Control chart—to measure customer’s critical to quality (CTQ) requirements
• Pareto chart—to focus the root cause analysis
• Fishbone (Ishikawa) diagram—to analyze the root causes of the problem
or symptom
With these three tools you can solve 80% to 90% of all problems associated
with defects or cost.
Problem-Solving Process
The Six Sigma Problem-Solving Process (Fig. 5-17) also follows the FISH model—
Focus, Improve, Sustain, and Honor. It focuses on identifying problems, determining
their root causes, and implementing countermeasures that will reduce or elim-
inate the waste, rework, and delay caused by these problems.
So let’s look at how to apply the problem-solving process to achieve Lean
Six Sigma improvements in quality and cost. The steps include