Page 75 - Lindens Handbook of Batteries
P. 75
2.32 PRINCIPLES OF OPERATION
4
2
Integrated capacity/Coulombs –2 0
–4
3.0 3.5 4.0 4.5
+
Potential vs. Li/Li /V
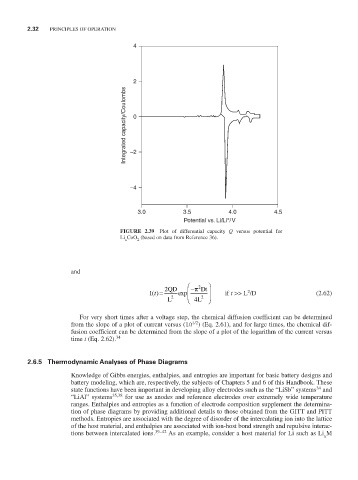
FIGURE 2.39 Plot of differential capacity Q versus potential for
Li CoO (based on data from Reference 36).
x
2
and
2 QD -π 2 Dt
I()= exp if t >> L /D (2.62)
2
t
L 2 4 L 2
For very short times after a voltage step, the chemical diffusion coefficient can be determined
1/2
from the slope of a plot of current versus (1/t ) (Eq. 2.61), and for large times, the chemical dif-
fusion coefficient can be determined from the slope of a plot of the logarithm of the current versus
34
time t (Eq. 2.62).
2.6.5 Thermodynamic Analyses of Phase Diagrams
Knowledge of Gibbs energies, enthalpies, and entropies are important for basic battery designs and
battery modeling, which are, respectively, the subjects of Chapters 5 and 6 of this Handbook. These
34
state functions have been important in developing alloy electrodes such as the “LiSb” systems and
“LiAl” systems 35,38 for use as anodes and reference electrodes over extremely wide temperature
ranges. Enthalpies and entropies as a function of electrode composition supplement the determina-
tion of phase diagrams by providing additional details to those obtained from the GITT and PITT
methods. Entropies are associated with the degree of disorder of the intercalating ion into the lattice
of the host material, and enthalpies are associated with ion-host bond strength and repulsive interac-
tions between intercalated ions. 39–42 As an example, consider a host material for Li such as Li M
x