Page 218 - Low Temperature Energy Systems with Applications of Renewable Energy
P. 218
Heating with geothermal systems 205
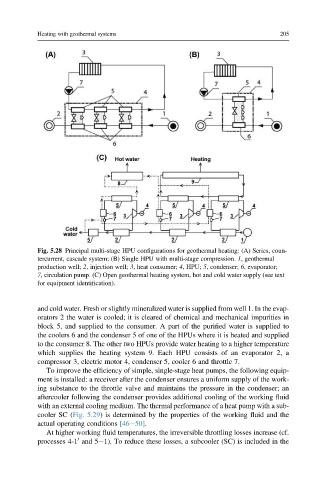
Fig. 5.28 Principal multi-stage HPU configurations for geothermal heating: (A) Series, coun-
tercurrent, cascade system; (B) Single HPU with multi-stage compression. 1, geothermal
production well; 2, injection well; 3, heat consumer; 4, HPU; 5, condenser; 6, evaporator;
7, circulation pump. (C) Open geothermal heating system, hot and cold water supply (see text
for equipment identification).
and cold water. Fresh or slightly mineralized water is supplied from well 1. In the evap-
orators 2 the water is cooled; it is cleared of chemical and mechanical impurities in
block 5, and supplied to the consumer. A part of the purified water is supplied to
the coolers 6 and the condenser 5 of one of the HPUs where it is heated and supplied
to the consumer 8. The other two HPUs provide water heating to a higher temperature
which supplies the heating system 9. Each HPU consists of an evaporator 2, a
compressor 3, electric motor 4, condenser 5, cooler 6 and throttle 7.
To improve the efficiency of simple, single-stage heat pumps, the following equip-
ment is installed: a receiver after the condenser ensures a uniform supply of the work-
ing substance to the throttle valve and maintains the pressure in the condenser; an
aftercooler following the condenser provides additional cooling of the working fluid
with an external cooling medium. The thermal performance of a heat pump with a sub-
cooler SC (Fig. 5.29) is determined by the properties of the working fluid and the
actual operating conditions [46e50].
At higher working fluid temperatures, the irreversible throttling losses increase (cf.
0
processes 4-1 and 5e1). To reduce these losses, a subcooler (SC) is included in the