Page 377 - 04. Subyek Engineering Materials - Manufacturing, Engineering and Technology SI 6th Edition - Serope Kalpakjian, Stephen Schmid (2009)
P. 377
Summary 357
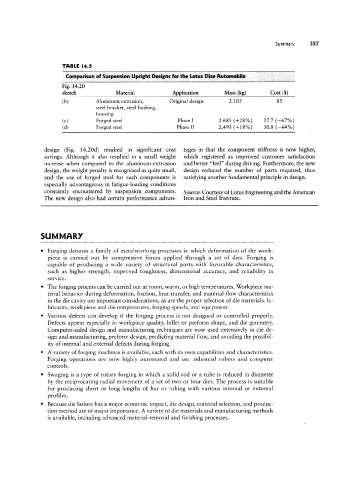
TABLE l4.5
Comparison of Suspension Upright Designs for the Lotus Elise Automobile
Fig. 14.20
sketch Material Application Mass (kg) Cost ($)
(b) Aluminum extrusion, Original design 2.105 85
steel bracket, steel bushing,
housing
(c) Forged steel Phase I 2.685 (+28%) 27.7 (-67%)
(d) Forged steel Phase II 2.493 (+18%) 30.8 (-64%)
design (Fig. 14.20d) resulted in significant cost tages in that the component stiffness is now higher,
savings. Although it also resulted in a small weight which registered as improved customer satisfaction
increase when compared to the aluminum-extrusion and better “feel” during driving. Furthermore, the new
design, the weight penalty is recognized as quite small, design reduced the number of parts required, thus
and the use of forged steel for such components is satisfying another fundamental principle in design.
especially advantageous in fatigue-loading conditions
constantly encountered by suspension components. Source: Courtesy of Louis Engineering and the American
The new design also had certain performance advan- Iron and Steel Institute.
SUMMARY
° Forging denotes a family of metalworking processes in which deformation of the work-
piece is carried out by compressive forces applied through a set of dies. Forging is
capable of producing a wide variety of structural parts with favorable characteristics,
such as higher strength, improved toughness, dimensional accuracy, and reliability in
service.
° The forging process can be carried out at room, warm, or high temperatures. Workpiece ma-
terial behavior during deformation, friction, heat transfer, and material-flow characteristics
in the die cavity are important considerations, as are the proper selection of die materials, lu-
bricants, workpiece and die temperatures, forging speeds, and equipment.
° Various defects can develop if the forging process is not designed or controlled properly.
Defects appear especially in workpiece quality, billet or preform shape, and die geometry.
Computer-aided design and manufacturing techniques are now used extensively in die de-
sign and manufacturing, preform design, predicting material flow, and avoiding the possibil-
ity of internal and external defects during forging.
° A variety of forging machines is available, each with its own capabilities and characteristics.
Forging operations are now highly automated and use industrial robots and computer
controls.
° Swaging is a type of rotary forging in which a solid rod or a tube is reduced in diameter
by the reciprocating radial movement of a set of two or four dies. The process is suitable
for producing short or long lengths of bar or tubing with various internal or external
profiles.
° Because die failure has a major economic impact, die design, material selection, and produc-
tion method are of major importance. A variety of die materials and manufacturing methods
is available, including advanced material-removal and finishing processes.