Page 124 - Materials Science and Engineering An Introduction
P. 124
96 • Chapter 3 / The Structure of Crystalline Solids
List of Symbols
Symbol Meaning
a Unit cell edge length for cubic structures; unit cell x-axial length
a 1 Vector head coordinate, hexagonal
a 1 Vector tail coordinate, hexagonal
A Atomic weight
A Planar intercept on x axis
d hkl Interplanar spacing for crystallographic planes having indices h, k, and l
n Order of reflection for x-ray diffraction
n Number of atoms associated with a unit cell
n Normalization factor—reduction of directional/planar indices to integers
23
N A Avogadro’s number (6.022 10 atoms/mol)
R Atomic radius
V C Unit cell volume
x 1 Vector tail coordinate
x 2 Vector head coordinate
l X-ray wavelength
r Density; theoretical density
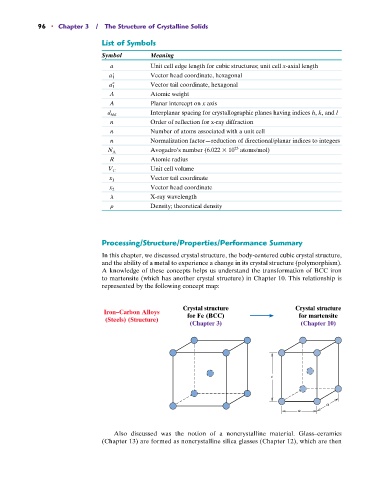
Processing/Structure/Properties/Performance Summary
In this chapter, we discussed crystal structure, the body-centered cubic crystal structure,
and the ability of a metal to experience a change in its crystal structure (polymorphism).
A knowledge of these concepts helps us understand the transformation of BCC iron
to martensite (which has another crystal structure) in Chapter 10. This relationship is
represented by the following concept map:
Crystal structure Crystal structure
Iron–Carbon Alloys
for Fe (BCC) for martensite
(Steels) (Structure)
(Chapter 3) (Chapter 10)
c
a
a
Also discussed was the notion of a noncrystalline material. Glass–ceramics
(Chapter 13) are formed as noncrystalline silica glasses (Chapter 12), which are then