Page 125 - Materials Science and Engineering An Introduction
P. 125
Questions and Problems • 97
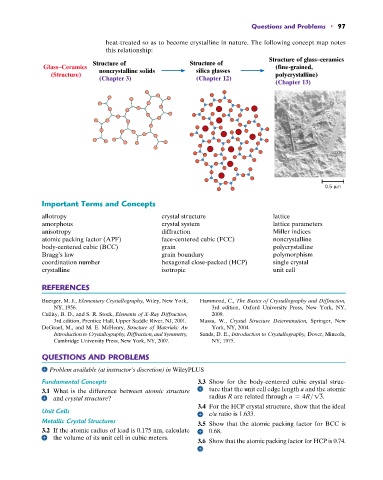
heat-treated so as to become crystalline in nature. The following concept map notes
this relationship:
Structure of glass–ceramics
Structure of Structure of
Glass–Ceramics noncrystalline solids silica glasses (fine-grained,
(Structure) polycrystalline)
(Chapter 3) (Chapter 12)
(Chapter 13)
m
0.5
0.5
m
Important Terms and Concepts
allotropy crystal structure lattice
amorphous crystal system lattice parameters
anisotropy diffraction Miller indices
atomic packing factor (APF) face-centered cubic (FCC) noncrystalline
body-centered cubic (BCC) grain polycrystalline
Bragg’s law grain boundary polymorphism
coordination number hexagonal close-packed (HCP) single crystal
crystalline isotropic unit cell
REFERENCES
Buerger, M. J., Elementary Crystallography, Wiley, New York, Hammond, C., The Basics of Crystallography and Diffraction,
NY, 1956. 3rd edition, Oxford University Press, New York, NY,
Cullity, B. D., and S. R. Stock, Elements of X-Ray Diffraction, 2009.
3rd edition, Prentice Hall, Upper Saddle River, NJ, 2001. Massa, W., Crystal Structure Determination, Springer, New
DeGraef, M., and M. E. McHenry, Structure of Materials: An York, NY, 2004.
Introduction to Crystallography, Diffraction, and Symmetry, Sands, D. E., Introduction to Crystallography, Dover, Mineola,
Cambridge University Press, New York, NY, 2007. NY, 1975.
QUESTIONS AND PROBLEMS
Problem available (at instructor’s discretion) in WileyPLUS
Fundamental Concepts 3.3 Show for the body-centered cubic crystal struc-
3.1 What is the difference between atomic structure ture that the unit cell edge length a and the atomic
and crystal structure? radius R are related through a = 4R> 13.
3.4 For the HCP crystal structure, show that the ideal
Unit Cells c/a ratio is 1.633.
Metallic Crystal Structures
3.5 Show that the atomic packing factor for BCC is
3.2 If the atomic radius of lead is 0.175 nm, calculate 0.68.
the volume of its unit cell in cubic meters.
3.6 Show that the atomic packing factor for HCP is 0.74.