Page 128 - Materials Science and Engineering An Introduction
P. 128
100 • Chapter 3 / The Structure of Crystalline Solids
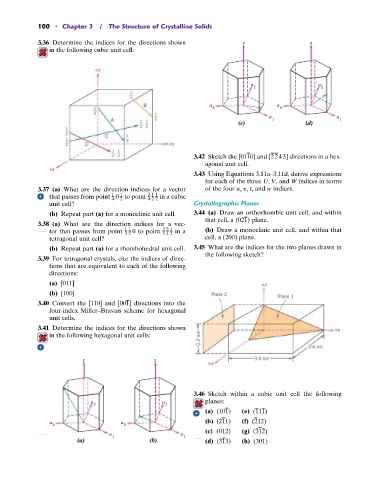
3.36 Determine the indices for the directions shown z z
in the following cubic unit cell:
a a
2 2
a a
3 3
a 1 a 1
(c) (d)
3.42 Sketch the [0110] and [2 2 4 3] directions in a hex-
agonal unit cell.
3.43 Using Equations 3.11a–3.11d, derive expressions
for each of the three U, V, and W indices in terms
3.37 (a) What are the direction indices for a vector of the four u, y, t, and w indices.
1
1
that passes from point 0 to point in a cubic
3 1 1
4
2
4 2 2
unit cell? Crystallographic Planes
(b) Repeat part (a) for a monoclinic unit cell. 3.44 (a) Draw an orthorhombic unit cell, and within
that cell, a (021) plane.
3.38 (a) What are the direction indices for a vec-
2 3 1
1 1
tor that passes from point 0 to point in a (b) Draw a monoclinic unit cell, and within that
3 2
3 4 2
tetragonal unit cell? cell, a (200) plane.
(b) Repeat part (a) for a rhombohedral unit cell. 3.45 What are the indices for the two planes drawn in
the following sketch?
3.39 For tetragonal crystals, cite the indices of direc-
tions that are equivalent to each of the following
directions:
(a) [011]
(b) [100]
3.40 Convert the [110] and [001] directions into the
four-index Miller–Bravais scheme for hexagonal
unit cells.
3.41 Determine the indices for the directions shown
in the following hexagonal unit cells:
z z
3.46 Sketch within a cubic unit cell the following
a a planes:
2 2
(a) (101) (e) (111)
(b) (211)
a a (f) (212)
3 3
(c) (012) (g) (312)
a 1 a 1
(a) (b) (d) (313) (h) (301)