Page 299 - Materials Science and Engineering An Introduction
P. 299
8.7 Cyclic Stresses • 271
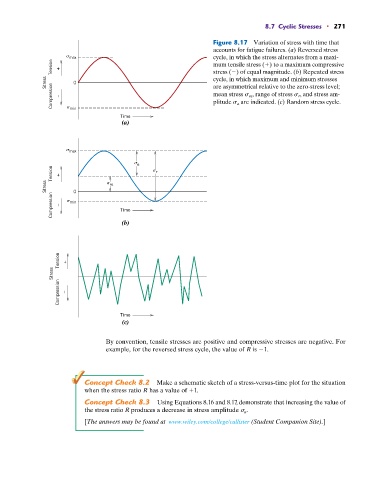
Figure 8.17 Variation of stress with time that
accounts for fatigue failures. (a) Reversed stress
max cycle, in which the stress alternates from a maxi-
Tension + mum tensile stress (
) to a maximum compressive
stress ( ) of equal magnitude. (b) Repeated stress
Stress 0 cycle, in which maximum and minimum stresses
Compression – mean stress s m , range of stress s r , and stress am-
are asymmetrical relative to the zero-stress level;
plitude s a are indicated. (c) Random stress cycle.
min
Time
(a)
max
a
Tension + r
Stress 0 m
Compression – min Time
(b)
Tension +
Stress
Compression –
Time
(c)
By convention, tensile stresses are positive and compressive stresses are negative. For
example, for the reversed stress cycle, the value of R is 1.
Concept Check 8.2 Make a schematic sketch of a stress-versus-time plot for the situation
when the stress ratio R has a value of
1.
Concept Check 8.3 Using Equations 8.16 and 8.17, demonstrate that increasing the value of
the stress ratio R produces a decrease in stress amplitude s a .
[The answers may be found at www.wiley.com/college/callister (Student Companion Site).]