Page 283 - Mechanical design of microresonators _ modeling and applications
P. 283
0-07-145538-8_CH05_282_08/30/05
Resonant Micromechanical Systems
282 Chapter Five
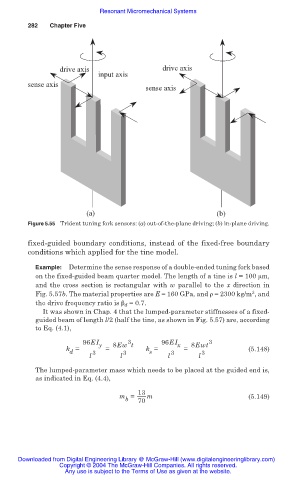
drive axis drive axis
input axis
sense axis
sense axis
(a) (b)
Figure 5.55 Trident tuning fork sensors: (a) out-of-the-plane driving; (b) in-plane driving.
fixed-guided boundary conditions, instead of the fixed-free boundary
conditions which applied for the tine model.
Example: Determine the sense response of a double-ended tuning fork based
on the fixed-guided beam quarter model. The length of a tine is l = 100 ȝm,
and the cross section is rectangular with w parallel to the x direction in
3
Fig. 5.57b. The material properties are E = 160 GPa, and ȡ = 2300 kg/m , and
the drive frequency ratio is ȕ d = 0.7.
It was shown in Chap. 4 that the lumped-parameter stiffnesses of a fixed-
guided beam of length l/2 (half the tine, as shown in Fig. 5.57) are, according
to Eq. (4.1),
96EI y 8Ew t 96EI x 8Ewt 3
3
k = = k = = (5.148)
s
d
l 3 l 3 l 3 l 3
The lumped-parameter mass which needs to be placed at the guided end is,
as indicated in Eq. (4.4),
13
m = m (5.149)
b 70
Downloaded from Digital Engineering Library @ McGraw-Hill (www.digitalengineeringlibrary.com)
Copyright © 2004 The McGraw-Hill Companies. All rights reserved.
Any use is subject to the Terms of Use as given at the website.