Page 284 - Mechanical design of microresonators _ modeling and applications
P. 284
0-07-145538-8_CH05_283_08/30/05
Resonant Micromechanical Systems
Resonant Micromechanical Systems 283
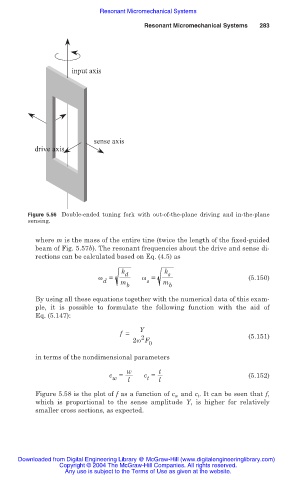
input axis
sense axis
drive axis
Figure 5.56 Double-ended tuning fork with out-of-the-plane driving and in-the-plane
sensing.
where m is the mass of the entire tine (twice the length of the fixed-guided
beam of Fig. 5.57b). The resonant frequencies about the drive and sense di-
rections can be calculated based on Eq. (4.5) as
k d k s
Ȧ = Ȧ = (5.150)
d m s m
b b
By using all these equations together with the numerical data of this exam-
ple, it is possible to formulate the following function with the aid of
Eq. (5.147):
Y
f = (5.151)
2
2Ȧ F
0
in terms of the nondimensional parameters
w t
c = c = (5.152)
w l t l
Figure 5.58 is the plot of f as a function of c w and c t . It can be seen that f,
which is proportional to the sense amplitude Y, is higher for relatively
smaller cross sections, as expected.
Downloaded from Digital Engineering Library @ McGraw-Hill (www.digitalengineeringlibrary.com)
Copyright © 2004 The McGraw-Hill Companies. All rights reserved.
Any use is subject to the Terms of Use as given at the website.