Page 288 - Mechanical design of microresonators _ modeling and applications
P. 288
0-07-145538-8_CH05_287_08/30/05
Resonant Micromechanical Systems
Resonant Micromechanical Systems 287
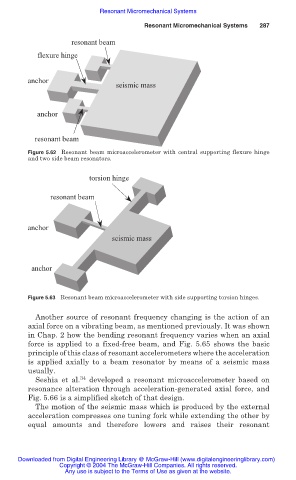
resonant beam
flexure hinge
anchor
seismic mass
anchor
resonant beam
Figure 5.62 Resonant beam microaccelerometer with central supporting flexure hinge
and two side beam resonators.
torsion hinge
resonant beam
anchor
seismic mass
anchor
Figure 5.63 Resonant beam microaccelerometer with side supporting torsion hinges.
Another source of resonant frequency changing is the action of an
axial force on a vibrating beam, as mentioned previously. It was shown
in Chap. 2 how the bending resonant frequency varies when an axial
force is applied to a fixed-free beam, and Fig. 5.65 shows the basic
principle of this class of resonant accelerometers where the acceleration
is applied axially to a beam resonator by means of a seismic mass
usually.
34
Seshia et al. developed a resonant microaccelerometer based on
resonance alteration through acceleration-generated axial force, and
Fig. 5.66 is a simplified sketch of that design.
The motion of the seismic mass which is produced by the external
acceleration compresses one tuning fork while extending the other by
equal amounts and therefore lowers and raises their resonant
Downloaded from Digital Engineering Library @ McGraw-Hill (www.digitalengineeringlibrary.com)
Copyright © 2004 The McGraw-Hill Companies. All rights reserved.
Any use is subject to the Terms of Use as given at the website.